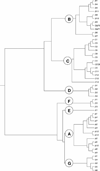
Human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family
- PMID: 19403462
- PMCID: PMC2752038
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-7364-3-3-281
Human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family
Abstract
There exist four fundamentally different classes of membrane-bound transport proteins: ion channels; transporters; aquaporins; and ATP-powered pumps. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are an example of ATP-dependent pumps. ABC transporters are ubiquitous membrane-bound proteins, present in all prokaryotes, as well as plants, fungi, yeast and animals. These pumps can move substrates in (influx) or out (efflux) of cells. In mammals, ABC transporters are expressed predominantly in the liver, intestine, blood-brain barrier, blood-testis barrier, placenta and kidney. ABC proteins transport a number of endogenous substrates, including inorganic anions, metal ions, peptides, amino acids, sugars and a large number of hydrophobic compounds and metabolites across the plasma membrane, and also across intracellular membranes. The human genome contains 49 ABC genes, arranged in eight subfamilies and named via divergent evolution. That ABC genes are important is underscored by the fact that mutations in at least 11 of these genes are already known to cause severe inherited diseases (eg cystic fibrosis and X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy [X-ALD]). ABC transporters also participate in the movement of most drugs and their metabolites across cell surface and cellular organelle membranes; thus, defects in these genes can be important in terms of cancer therapy, pharmacokinetics and innumerable pharmacogenetic disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolution of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily in vertebrates.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2005;6:123-42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.6.080604.162122. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 16124856 Review.
-
Plant ABC transporters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 1;1465(1-2):79-103. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(00)00132-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10748248 Review.
-
Towards Identification of the Substrates of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters.Plant Physiol. 2018 Sep;178(1):18-39. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00325. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29987003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in human metabolism and diseases.Physiol Res. 2004;53(3):235-43. Physiol Res. 2004. PMID: 15209530 Review.
-
The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily.J Lipid Res. 2001 Jul;42(7):1007-17. J Lipid Res. 2001. PMID: 11441126 Review.
Cited by
-
The lysosomal protein ABCD4 can transport vitamin B12 across liposomal membranes in vitro.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100654. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100654. Epub 2021 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33845046 Free PMC article.
-
Efflux ABC transporters in drug disposition and their posttranscriptional gene regulation by microRNAs.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 24;15:1423416. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423416. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39114355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GW583340 and GW2974, human EGFR and HER-2 inhibitors, reverse ABCG2- and ABCB1-mediated drug resistance.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Jun 15;83(12):1613-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.02.028. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22414725 Free PMC article.
-
Plant ABC Transporters.Arabidopsis Book. 2011;9:e0153. doi: 10.1199/tab.0153. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Arabidopsis Book. 2011. PMID: 22303277 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer stem cells and strategies for targeted drug delivery.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021 Oct;11(5):1779-1805. doi: 10.1007/s13346-020-00863-9. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33095384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Camerino DC, Desaphy JF, Tricarico D. et al.Therapeutic approaches to ion channel diseases. Adv Genet. 2008;64:81–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources