Regulation of H3K4 trimethylation via Cps40 (Spp1) of COMPASS is monoubiquitination independent: implication for a Phe/Tyr switch by the catalytic domain of Set1
- PMID: 19398585
- PMCID: PMC2698764
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00013-09
Regulation of H3K4 trimethylation via Cps40 (Spp1) of COMPASS is monoubiquitination independent: implication for a Phe/Tyr switch by the catalytic domain of Set1
Abstract
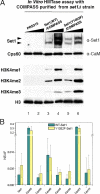
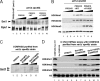
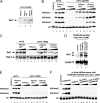
The multiprotein complex Set1/COMPASS is the founding member of the histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferases, whose human homologs include the MLL and hSet1 complexes. COMPASS can mono-, di-, and trimethylate H3K4, but transitioning to di- and trimethylation requires prior H2B monoubiquitination followed by recruitment of the Cps35 (Swd2) subunit of COMPASS. Another subunit, Cps40 (Spp1), interacts directly with Set1 and is only required for transitioning to trimethylation. To investigate how the Set1 and COMPASS subunits establish the methylation states of H3K4, we generated a homology model of the catalytic domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast Set1 and identified several key residues within the Set1 catalytic pocket that are capable of regulating COMPASS's activity. We show that Tyr1052, a putative Phe/Tyr switch of Set1, plays an essential role in the regulation of H3K4 trimethylation by COMPASS and that the mutation to phenylalanine (Y1052F) suppresses the loss of Cps40 in H3K4 trimethylation levels, suggesting that Tyr1052 functions together with Cps40. However, the loss of H2B monoubiquitination is not suppressed by this mutation, while Cps40 is stably assembled in COMPASS on chromatin, demonstrating that Tyr1052- and Cps40-mediated H3K4 trimethylation takes place following and independently of H2B monoubiquitination. Our studies provide a molecular basis for the way in which H3K4 trimethylation is regulated by Tyr1052 and the Cps40 subunit of COMPASS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Context dependency of Set1/COMPASS-mediated histone H3 Lys4 trimethylation.Genes Dev. 2014 Jan 15;28(2):115-20. doi: 10.1101/gad.232215.113. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24402317 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitylation of the COMPASS component Swd2 links H2B ubiquitylation to H3K4 trimethylation.Nat Cell Biol. 2008 Nov;10(11):1365-71. doi: 10.1038/ncb1796. Epub 2008 Oct 12. Nat Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18849979
-
Histone crosstalk between H2B monoubiquitination and H3 methylation mediated by COMPASS.Cell. 2007 Dec 14;131(6):1084-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.046. Cell. 2007. PMID: 18083099
-
Structural basis for H3K4 trimethylation by yeast Set1/COMPASS.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2010;50(1):104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2009.12.005. Epub 2009 Dec 18. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2010. PMID: 20005892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spp1 at the crossroads of H3K4me3 regulation and meiotic recombination.Epigenetics. 2013 Apr;8(4):355-60. doi: 10.4161/epi.24295. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Epigenetics. 2013. PMID: 23511748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
WRAD: enabler of the SET1-family of H3K4 methyltransferases.Brief Funct Genomics. 2012 May;11(3):217-26. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/els017. Epub 2012 May 30. Brief Funct Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22652693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cross-Regulation Between Set1, Clr4, and Lsd1/2 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.PLoS Genet. 2024 Jan 5;20(1):e1011107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011107. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38181050 Free PMC article.
-
Methylated H3K4, a transcription-associated histone modification, is involved in the DNA damage response pathway.PLoS Genet. 2010 Aug 26;6(8):e1001082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001082. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20865123 Free PMC article.
-
Set1/COMPASS and Mediator are repurposed to promote epigenetic transcriptional memory.Elife. 2016 Jun 23;5:e16691. doi: 10.7554/eLife.16691. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27336723 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Relevance of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in Cervix Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;15(20):4952. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204952. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brunger, A. T., P. D. Adams, G. M. Clore, W. L. DeLano, P. Gros, R. W. Grosse-Kunstleve, J. S. Jiang, J. Kuszewski, M. Nilges, N. S. Pannu, R. J. Read, L. M. Rice, T. Simonson, and G. L. Warren. 1998. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54905-921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
