Signalling pathways in alcohol-induced liver inflammation
- PMID: 19398236
- PMCID: PMC3342816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.03.007
Signalling pathways in alcohol-induced liver inflammation
Abstract
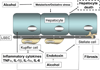
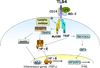
The pathogenesis of alcoholic liver injury involves interactions of several intracellular signalling pathways in different cell types of the liver. Alcohol-induced sensitization of liver macrophages to portal endotoxin/lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is considered a hallmark of alcoholic liver disease (ALD). Intracellular mechanisms associated with LPS-induced signalling play a crucial role in the initiation and progression of alcoholic liver injury, and are being extensively explored. LPS recognition by Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) on macrophages and other cell types in the liver, activation of downstream signalling pathways culminating in activation of transcription factors such as NFkappaB, AP-1 leads to increased inflammatory cytokine production in ALD. In addition, LPS-induced MAPK such as ERK and p38 also contribute to liver injury. The importance of alcohol-induced reactive oxygen species and interactions with TLR pathways in macrophages leading to inflammation is becoming increasingly evident. Collectively, these signalling pathways induce pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines that play an important role in ALD. In this review we describe the key signalling intermediates leading to alcohol-induced inflammation in alcoholic liver disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Common pathogenic mechanism in development progression of liver injury caused by non-alcoholic or alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Toxicol Sci. 2007 Dec;32(5):453-68. doi: 10.2131/jts.32.453. J Toxicol Sci. 2007. PMID: 18198478 Review.
-
Ethanol-induced sensitization to endotoxin in Kupffer cells is dependent upon oxidative stress.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Dec;29(12 Suppl):246S-50S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000191128.54871.40. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16385231
-
Recent insights into the role of the innate immune system in the development of alcoholic liver disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2003 Sep;228(8):882-90. doi: 10.1177/153537020322800803. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2003. PMID: 12968059 Review.
-
Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: role of oxidative metabolism.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 21;20(47):17756-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17756. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25548474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory pathways and alcoholic liver disease: role of an adiponectin/interleukin-10/heme oxygenase-1 pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Mar 21;16(11):1330-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1330. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20238399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review on Biological Characteristics of Kv1.3 and Its Role in Liver Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 21;12:652508. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.652508. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34093186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial dysfunction in cirrhosis: Role of inflammation and oxidative stress.World J Hepatol. 2015 Mar 27;7(3):443-59. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.443. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25848469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigallocatechin Gallate Can Protect Mice From Acute Stress Induced by LPS While Stabilizing Gut Microbes and Serum Metabolites Levels.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 1;12:640305. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.640305. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868268 Free PMC article.
-
Binge ethanol and liver: new molecular developments.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013 Apr;37(4):550-7. doi: 10.1111/acer.12011. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013. PMID: 23347137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of Fucoxanthin against Alcoholic Liver Injury by Activation of Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Defense and Inhibition of TLR4-Mediated Inflammation.Mar Drugs. 2019 Sep 27;17(10):552. doi: 10.3390/md17100552. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31569771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hines IN, Wheeler MD. Recent advances in alcoholic liver disease III. Role of innate immune responses in alcoholic hepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G310–G314. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto M, Uemura M, Nakatani Y, Tsujita S, Hoppo K, Tamagawa T, et al. Plasma endotoxin and serum cytokine levels in patients with alcoholic hepatitis: relation to severity of Liver disturbance. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:48S–54S. - PubMed
-
- McClain CJ, Cohen DA. Increased tumor necrosis factor production by monocytes in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology. 1989;9:349–351. - PubMed
-
- Khoruts A, Stahnke L, McClain CJ, Logan G, Allen J. Circulating tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 concentrations in chronic alcoholic patients. Hepatology. 1991;13:267–276. - PubMed
-
- Thakur V, McMullen MR, Ptritchard MT, Nagy LE. Regulation of macrophage activation in alcoholic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22(suppl 1):S53–S56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

