Bmi-1 regulates the Ink4a/Arf locus to control pancreatic beta-cell proliferation
- PMID: 19390085
- PMCID: PMC2675870
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1742609
Bmi-1 regulates the Ink4a/Arf locus to control pancreatic beta-cell proliferation
Abstract
The molecular mechanisms that regulate the age-induced increase of p16(INK4a) expression associated with decreased beta-cell proliferation and regeneration are not well understood. We report that in aged islets, derepression of the Ink4a/Arf locus is associated with decreased Bmi-1 binding, loss of H2A ubiquitylation, increased MLL1 recruitment, and a concomitant increase in H3K4 trimethylation. During beta-cell regeneration these histone modifications are reversed resulting in reduced p16(INK4a) expression and increased proliferation. We suggest that PcG and TrxG proteins impart a combinatorial code of histone modifications on the Ink4a/Arf locus to control beta-cell proliferation during aging and regeneration.
Figures
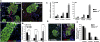
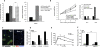
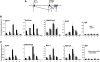
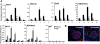
Similar articles
-
Polycomb protein Ezh2 regulates pancreatic beta-cell Ink4a/Arf expression and regeneration in diabetes mellitus.Genes Dev. 2009 Apr 15;23(8):975-85. doi: 10.1101/gad.1742509. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19390090 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb mediated epigenetic silencing and replication timing at the INK4a/ARF locus during senescence.PLoS One. 2009 May 20;4(5):e5622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005622. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19462008 Free PMC article.
-
A novel zinc finger protein Zfp277 mediates transcriptional repression of the Ink4a/arf locus through polycomb repressive complex 1.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 24;5(8):e12373. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012373. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808772 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell self-renewal and cancer cell proliferation are regulated by common networks that balance the activation of proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressors.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:177-85. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2005.70.057. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005. PMID: 16869752 Review.
-
Role of Ink4a/Arf locus in beta cell mass expansion under physiological and pathological conditions.J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:873679. doi: 10.1155/2014/873679. Epub 2014 Feb 6. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 24672805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance of cell cycle inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma.Med Mol Morphol. 2013 Dec;46(4):185-92. doi: 10.1007/s00795-013-0047-7. Epub 2013 May 3. Med Mol Morphol. 2013. PMID: 23640750 Review.
-
Bmi1 enhances tumorigenicity and cancer stem cell function in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055820. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437065 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal development, maturation and aging in the mouse cochlea and their effects on hair cell regeneration.Hear Res. 2013 Mar;297:68-83. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.009. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23164734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of linear and novel circular forms of an INK4/ARF-associated non-coding RNA correlates with atherosclerosis risk.PLoS Genet. 2010 Dec 2;6(12):e1001233. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001233. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21151960 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic cancer prevention mechanisms in skin cancer.AAPS J. 2013 Oct;15(4):1064-71. doi: 10.1208/s12248-013-9513-3. Epub 2013 Aug 1. AAPS J. 2013. PMID: 23904153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bracken A.P., Kleine-Kohlbrecher D., Dietrich N., Pasini D., Gargiulo G., Beekman C., Theilgaard-Monch K., Minucci S., Porse B.T., Marine J.C., et al. The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A–ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells. Genes & Dev. 2007;21:525–530. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruggeman S.W., Valk-Lingbeek M.E., van der Stoop P.P., Jacobs J.J., Kieboom K., Tanger E., Hulsman D., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., et al. Ink4a and Arf differentially affect cell proliferation and neural stem cell self-renewal in Bmi1-deficient mice. Genes & Dev. 2005;19:1438–1443. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao R., Tsukada Y., Zhang Y. Role of Bmi-1 and Ring1A in H2A ubiquitylation and Hox gene silencing. Mol. Cell. 2005;20:845–854. - PubMed
-
- Dor Y., Brown J., Martinez O.I., Melton D.A. Adult pancreatic β-cells are formed by self-duplication rather than stem-cell differentiation. Nature. 2004;429:41–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
