Overexpression of an activated REL mutant enhances the transformed state of the human B-lymphoma BJAB cell line and alters its gene expression profile
- PMID: 19377508
- PMCID: PMC2796798
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.74
Overexpression of an activated REL mutant enhances the transformed state of the human B-lymphoma BJAB cell line and alters its gene expression profile
Abstract
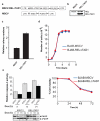
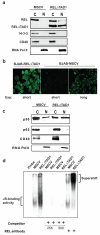
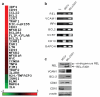
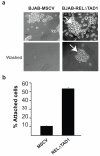
The human REL proto-oncogene encodes a transcription factor in the nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB family. Overexpression of REL is acutely transforming in chicken lymphoid cells, but has not been shown to transform any mammalian lymphoid cell type. In this report, we show that overexpression of a highly transforming mutant of REL (RELDeltaTAD1) increases the oncogenic properties of the human B-cell lymphoma BJAB cell line, as shown by increased colony formation in soft agar, tumor formation in SCID (severe combined immunodeficient) mice, and adhesion. BJAB-RELDeltaTAD1 cells also show decreased activation of caspase in response to doxorubicin. BJAB-RELDeltaTAD1 cells have increased levels of active nuclear REL protein as determined by immunofluorescence, subcellular fractionation and electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Overexpression of RELDeltaTAD1 in BJAB cells has transformed the gene expression profile of BJAB cells from that of a germinal center B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (GCB-DLBCL) to that of an activated B-cell subtype (ABC-DLBCL), as evidenced by increased expression of many ABC-defining mRNAs. Upregulated genes in BJAB-RELDeltaTAD1 cells include several NF-kappaB targets that encode proteins previously implicated in B-cell development or oncogenesis, including BCL2, IRF4, CD40 and VCAM1. The cell system we describe here may be valuable for further characterizing the molecular details of REL-induced lymphoma in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NF-kappaB down-regulates expression of the B-lymphoma marker CD10 through a miR-155/PU.1 pathway.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 21;286(3):1675-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.177063. Epub 2010 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 20947507 Free PMC article.
-
The NF-κB subunit c-Rel regulates Bach2 tumour suppressor expression in B-cell lymphoma.Oncogene. 2016 Jun 30;35(26):3476-84. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.399. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26522720 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of an IKK phosphorylation site within the transactivation domain of REL in two patients with B-cell lymphoma enhances REL's in vitro transforming activity.Oncogene. 2007 Apr 26;26(19):2685-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210089. Epub 2006 Oct 30. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17072339
-
Regulation of B-cell function by NF-kappaB c-Rel in health and disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Sep;77(17):3325-3340. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03488-w. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32130429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The c-Rel transcription factor and B-cell proliferation: a deal with the devil.Oncogene. 2004 Mar 25;23(13):2275-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207410. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 14755244 Review.
Cited by
-
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E is a direct transcriptional target of NF-κB and is aberrantly regulated in acute myeloid leukemia.Leukemia. 2013 Oct;27(10):2047-55. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.73. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Leukemia. 2013. PMID: 23467026 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB down-regulates expression of the B-lymphoma marker CD10 through a miR-155/PU.1 pathway.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 21;286(3):1675-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.177063. Epub 2010 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 20947507 Free PMC article.
-
Annotation enrichment analysis: an alternative method for evaluating the functional properties of gene sets.Sci Rep. 2014 Feb 26;4:4191. doi: 10.1038/srep04191. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24569707 Free PMC article.
-
The NF-κB subunit c-Rel regulates Bach2 tumour suppressor expression in B-cell lymphoma.Oncogene. 2016 Jun 30;35(26):3476-84. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.399. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26522720 Free PMC article.
-
Histone acetyltransferase-deficient p300 mutants in diffuse large B cell lymphoma have altered transcriptional regulatory activities and are required for optimal cell growth.Mol Cancer. 2014 Feb 15;13:29. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-29. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24529102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Barth TF, Martin-Subero JI, Joos S, Menz CK, Hasel C, Mechtersheimer G, et al. Gains of 2p involving the REL locus correlate with nuclear c-Rel protein accumulation in neoplastic cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2003;101:3681–3686. - PubMed
-
- Dierlamm J, Murga Penas EM, Bentink S, Wessendorf S, Berger H, Hummel M, et al. Gain of chromosome region 18q21 including the MALT1 gene is associated with the activated B-cell-like gene expression subtype and increased BCL2 gene dosage and protein expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2008;93:688–696. - PubMed
-
- Enberg I, Klein G, Biovanella BC, Stehlin J, McCormick KJ, Andersson-Anvret M, et al. Relationship between the amounts of EBV-DNA and EBNA per cell, clonability and tumorigenicity in two EBV-negative lymphoma lines and their EBV-converted cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1983;31:163–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

