Control of transcriptional elongation and cotranscriptional histone modification by the yeast BUR kinase substrate Spt5
- PMID: 19365074
- PMCID: PMC2678430
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806302106
Control of transcriptional elongation and cotranscriptional histone modification by the yeast BUR kinase substrate Spt5
Abstract
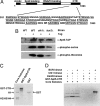
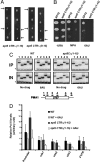
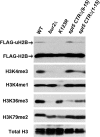
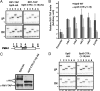
Elongation by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) is a finely regulated process in which many elongation factors contribute to gene regulation. Among these factors are the polymerase-associated factor (PAF) complex, which associates with RNAPII, and several cyclin-dependent kinases, including positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) in humans and BUR kinase (Bur1-Bur2) and C-terminal domain (CTD) kinase 1 (CTDK1) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. An important target of P-TEFb and CTDK1, but not BUR kinase, is the CTD of the Rpb1 subunit of RNAPII. Although the essential BUR kinase phosphorylates Rad6, which is required for histone H2B ubiquitination on K123, Rad6 is not essential, leaving a critical substrate(s) of BUR kinase unidentified. Here we show that BUR kinase is important for the phosphorylation in vivo of Spt5, a subunit of the essential yeast RNAPII elongation factor Spt4/Spt5, whose human orthologue is DRB sensitivity-inducing factor. BUR kinase can also phosphorylate the C-terminal region (CTR) of Spt5 in vitro. Like BUR kinase, the Spt5 CTR is important for promoting elongation by RNAPII and recruiting the PAF complex to transcribed regions. Also like BUR kinase and the PAF complex, the Spt5 CTR is important for histone H2B K123 monoubiquitination and histone H3 K4 and K36 trimethylation during transcription elongation. Our results suggest that the Spt5 CTR, which contains 15 repeats of a hexapeptide whose consensus sequence is S[T/A]WGG[A/Q], is a substrate of BUR kinase and a platform for the association of proteins that promote both transcription elongation and histone modification in transcribed regions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of the transcription elongation factor Spt5 by yeast Bur1 kinase stimulates recruitment of the PAF complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Sep;29(17):4852-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00609-09. Epub 2009 Jul 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19581288 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Analysis of Yeast Suppressor of Ty 4/5 (Spt4/5) Reveals the Importance of Nucleic Acid Interactions in the Prevention of RNA Polymerase II Arrest.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 6;291(19):9853-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.716001. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26945063 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal repeat domain of Spt5 plays an important role in suppression of Rad26-independent transcription coupled repair.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5317-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082818. Epub 2009 Dec 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20042611 Free PMC article.
-
Bur1/Bur2 and the Ctk complex in yeast: the split personality of mammalian P-TEFb.Cell Cycle. 2006 May;5(10):1066-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.10.2769. Epub 2006 May 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16721054 Review.
-
The Spt4-Spt5 complex: a multi-faceted regulator of transcription elongation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):105-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22982195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pol II CTD kinases Bur1 and Kin28 promote Spt5 CTR-independent recruitment of Paf1 complex.EMBO J. 2012 Aug 15;31(16):3494-505. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.188. Epub 2012 Jul 13. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22796944 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture of the RNA polymerase-Spt4/5 complex and basis of universal transcription processivity.EMBO J. 2011 Apr 6;30(7):1302-10. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.64. Epub 2011 Mar 8. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21386817 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II transcription elongation and Pol II CTD Ser2 phosphorylation: A tail of two kinases.Nucleus. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):224-36. doi: 10.4161/nucl.29347. Epub 2014 May 30. Nucleus. 2014. PMID: 24879308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cdc73 subunit of Paf1 complex contains C-terminal Ras-like domain that promotes association of Paf1 complex with chromatin.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 30;287(14):10863-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.325647. Epub 2012 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22318720 Free PMC article.
-
A functional interface at the rDNA connects rRNA synthesis, pre-rRNA processing and nucleolar surveillance in budding yeast.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024962. Epub 2011 Sep 19. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21949810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saunders A, Core LJ, Lis JT. Breaking barriers to transcription elongation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:557–567. - PubMed
-
- Peterlin BM, Price DH. Controlling the elongation phase of transcription with P-TEFb. Mol Cell. 2006;23:297–305. - PubMed
-
- Price DH. Poised polymerases: On your mark… get set… go! Mol Cell. 2008;30:7–10. - PubMed
-
- Phatnani HP, Greenleaf AL. Phosphorylation and functions of the RNA polymerase II CTD. Genes Dev. 2006;20:2922–2936. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

