Oxidation-specific epitopes are dominant targets of innate natural antibodies in mice and humans
- PMID: 19363291
- PMCID: PMC2673862
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI36800
Oxidation-specific epitopes are dominant targets of innate natural antibodies in mice and humans
Abstract
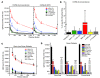
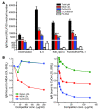
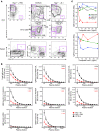
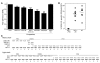
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the accumulation of oxidized lipoproteins and apoptotic cells. Adaptive immune responses to various oxidation-specific epitopes play an important role in atherogenesis. However, accumulating evidence suggests that these epitopes are also recognized by innate receptors, such as scavenger receptors on macrophages, and plasma proteins, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). Here, we provide multiple lines of evidence that oxidation-specific epitopes constitute a dominant, previously unrecognized target of natural Abs (NAbs) in both mice and humans. Using reconstituted mice expressing solely IgM NAbs, we have shown that approximately 30% of all NAbs bound to model oxidation-specific epitopes, as well as to atherosclerotic lesions and apoptotic cells. Because oxidative processes are ubiquitous, we hypothesized that these epitopes exert selective pressure to expand NAbs, which in turn play an important role in mediating homeostatic functions consequent to inflammation and cell death, as demonstrated by their ability to facilitate apoptotic cell clearance. These findings provide novel insights into the functions of NAbs in mediating host homeostasis and into their roles in health and diseases, such as chronic inflammatory diseases and atherosclerosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
B-1b Cells Secrete Atheroprotective IgM and Attenuate Atherosclerosis.Circ Res. 2015 Jul 17;117(3):e28-39. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.306044. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 26082558 Free PMC article.
-
Natural IgM antibodies against oxidation-specific epitopes.J Clin Immunol. 2010 May;30 Suppl 1:S56-60. doi: 10.1007/s10875-010-9396-3. J Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20387104 Review.
-
Oxidation-specific epitopes are important targets of innate immunity.J Intern Med. 2008 May;263(5):479-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2008.01968.x. J Intern Med. 2008. PMID: 18410591 Review.
-
IL-5 links adaptive and natural immunity specific for epitopes of oxidized LDL and protects from atherosclerosis.J Clin Invest. 2004 Aug;114(3):427-37. doi: 10.1172/JCI20479. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15286809 Free PMC article.
-
ABCG1 is required for pulmonary B-1 B cell and natural antibody homeostasis.J Immunol. 2014 Dec 1;193(11):5637-48. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400606. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25339664 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory mediators in vascular disease: identifying promising targets for intracranial aneurysm research.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:896283. doi: 10.1155/2015/896283. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25922566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Relationship Between Different IgG and IgA Anti-Modified Protein Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2021 May 20;12:627986. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.627986. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093522 Free PMC article.
-
Redox control of inflammation in macrophages.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Aug 20;19(6):595-637. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4785. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 23311665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ApoB-Specific CD4+ T Cells in Mouse and Human Atherosclerosis.Cells. 2021 Feb 19;10(2):446. doi: 10.3390/cells10020446. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33669769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Natural Autoantibodies and Natural IgM Anti-Leucocyte Autoantibodies in Health and Disease.Front Immunol. 2016 Jun 6;7:198. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00198. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27375614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Binder C.J., et al. Innate and acquired immunity in atherogenesis. Nat. Med. 2002;8:1218–1226. - PubMed
-
- Hansson G.K., Libby P. The immune response in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006;6:508–519. - PubMed
-
- Getz G.S., Vanderlaan P.A., Reardon C.A. The immune system and murine atherosclerosis. Curr. Drug Targets. 2007;8:1297–1306. - PubMed
-
- Binder C.J., et al. The role of natural antibodies in atherogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 2005;46:1353–1363. - PubMed
-
- Boullier A., et al. Phosphocholine as a pattern recognition ligand for CD36. J. Lipid Res. 2005;46:969–976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

