Nuclear factor-kappaB enhances ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and neoangiogenesis in vivo
- PMID: 19349372
- PMCID: PMC2671278
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080706
Nuclear factor-kappaB enhances ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and neoangiogenesis in vivo
Abstract
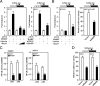
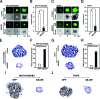
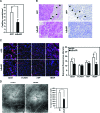
The (HER2/Neu) ErbB2 oncogene is commonly overexpressed in human breast cancer and is sufficient for mammary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. Nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activity is increased in both human and murine breast tumors. The immune response to mammary tumorigenesis may regulate tumor progression. The role of endogenous mammary epithelial cell NF-kappaB had not previously been determined in immune-competent animals. Furthermore, the role of the NF-kappaB components, p50 and p65, in tumor growth was not known. Herein, the expression of a stabilized form of the NF-kappaB-inhibiting IkappaBalpha protein (IkappaBalphaSR) in breast tumor cell lines that express oncogenic ErbB2 inhibited DNA synthesis and growth in both two- and three-dimensional cultures. Either NF-kappaB inhibition or selective silencing of p50 or p65 led to a loss of contact-independent tumor growth in vitro. IkappaBalphaSR reversed the features of the oncogene-induced phenotype under three-dimensional growth conditions. The NF-kappaB blockade inhibited ErbB2-induced mammary tumor growth in both immune-competent and immune-deficient mice. These findings were associated with both reduced tumor microvascular density and a reduction in the amount of vascular endothelial growth factor. The expression of IkappaBalphaSR in breast cancer tumors inhibited angiogenesis. Thus, mammary epithelial cell NF-kappaB activity enhances ErbB2-mediated mammary tumorigenesis in vivo by promoting both growth and survival signaling via the promotion of tumor vasculogenesis.
Figures
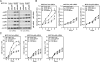
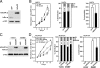

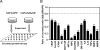
Similar articles
-
The canonical NF-kappaB pathway governs mammary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice and tumor stem cell expansion.Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 15;70(24):10464-73. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0732. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21159656 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-D inhibits cell growth and angiogenesis through inactivation of Notch-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling.Cancer Res. 2007 Dec 1;67(23):11377-85. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2803. Cancer Res. 2007. Retraction in: Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 15;78(18):5469. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1173. PMID: 18056465 Retracted.
-
Her-2/neu overexpression induces NF-kappaB via a PI3-kinase/Akt pathway involving calpain-mediated degradation of IkappaB-alpha that can be inhibited by the tumor suppressor PTEN.Oncogene. 2001 Mar 15;20(11):1287-99. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204257. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11313873
-
NF-κB: a mediator that promotes or inhibits angiogenesis in human diseases?Expert Rev Mol Med. 2023 Jul 28;25:e25. doi: 10.1017/erm.2023.20. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37503730 Review.
-
The tumor suppressor function of STAT1 in breast cancer.JAKSTAT. 2013 Apr 1;2(2):e23353. doi: 10.4161/jkst.23353. JAKSTAT. 2013. PMID: 24058806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylation of the cell-fate factor dachshund determines p53 binding and signaling modules in breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2013 Jun;4(6):923-35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1094. Oncotarget. 2013. PMID: 23798621 Free PMC article.
-
CCL5 promotes breast cancer recurrence through macrophage recruitment in residual tumors.Elife. 2019 Apr 16;8:e43653. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43653. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30990165 Free PMC article.
-
Local immune regulatory effects of Bangdeyun on the endometrium of mice with embryo implantation dysfunction during the implantation time.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2009 Jun;29(3):372-6. doi: 10.1007/s11596-009-0322-y. Epub 2009 Jun 10. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 19513625
-
The role of breast cancer stem cells in metastasis and therapeutic implications.Am J Pathol. 2011 Jul;179(1):2-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.005. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21640330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappaB is preferentially involved in the proliferation of basal-like subtype breast cancer cell lines.Cancer Sci. 2009 Sep;100(9):1668-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01228.x. Epub 2009 May 28. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19538528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghosh S, Karin M. Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell. 2002;109:S81–S96. - PubMed
-
- Thanos D, Maniatis T. NF-κB: a lesson in family values. Cell. 1995;80:529–532. - PubMed
-
- Senftleben U, Cao Y, Xiao G, Greten FR, Krahn G, Bonizzi G, Chen Y, Hu Y, Fong A, Sun SC, Karin M. Activation by IKKalpha of a second, evolutionary conserved NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Science. 2001;293:1495–1499. - PubMed
-
- Eaden J, Abrams K, Ekbom A, Jackson E, Mayberry J. Colorectal cancer prevention in ulcerative colitis: a case-control study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000;14:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Dajee M, Lazarov M, Zhang JY, Cai T, Green CL, Russell AJ, Marinkovich MP, Tao S, Lin Q, Kubo Y, Khavari PA. NF-kappaB blockade and oncogenic Ras trigger invasive human epidermal neoplasia. Nature. 2003;421:639–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

