Bile acids as regulatory molecules
- PMID: 19346331
- PMCID: PMC2724047
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R900007-JLR200
Bile acids as regulatory molecules
Abstract
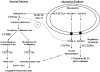
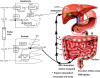
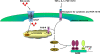
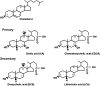
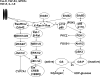
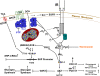
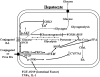
In the past, bile acids were considered to be just detergent molecules derived from cholesterol in the liver. They were known to be important for the solubilization of cholesterol in the gallbladder and for stimulating the absorption of cholesterol, fat-soluble vitamins, and lipids from the intestines. However, during the last two decades, it has been discovered that bile acids are regulatory molecules. Bile acids have been discovered to activate specific nuclear receptors (farnesoid X receptor, preganane X receptor, and vitamin D receptor), G protein coupled receptor TGR5 (TGR5), and cell signaling pathways (c-jun N-terminal kinase 1/2, AKT, and ERK 1/2) in cells in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Activation of nuclear receptors and cell signaling pathways alter the expression of numerous genes encoding enzyme/proteins involved in the regulation of bile acid, glucose, fatty acid, lipoprotein synthesis, metabolism, transport, and energy metabolism. They also play a role in the regulation of serum triglyceride levels in humans and rodents. Bile acids appear to function as nutrient signaling molecules primarily during the feed/fast cycle as there is a flux of these molecules returning from the intestines to the liver following a meal. In this review, we will summarize the current knowledge of how bile acids regulate hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism through the activation of specific nuclear receptors and cell signaling pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bile acids as regulators of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism.Dig Dis. 2010;28(1):220-4. doi: 10.1159/000282091. Epub 2010 May 7. Dig Dis. 2010. PMID: 20460915 Review.
-
Bile acid metabolism and signaling.Compr Physiol. 2013 Jul;3(3):1191-212. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c120023. Compr Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23897684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile acids are nutrient signaling hormones.Steroids. 2014 Aug;86:62-8. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2014.04.016. Epub 2014 May 10. Steroids. 2014. PMID: 24819989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocrine functions of bile acids.EMBO J. 2006 Apr 5;25(7):1419-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601049. Epub 2006 Mar 16. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16541101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Farnesoid X receptor induces Takeda G-protein receptor 5 cross-talk to regulate bile acid synthesis and hepatic metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 30;292(26):11055-11069. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.784322. Epub 2017 May 6. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28478385 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of deoxycholylglycine, a conjugated secondary bile acid, on myogenic tone and agonist-induced contraction in rat resistance arteries.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032006. Epub 2012 Feb 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22359652 Free PMC article.
-
Choline metabolism provides novel insights into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its progression.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar;28(2):159-65. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e32834e7b4b. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22134222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Pathogenesis of NASH.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 20;17(9):1575. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091575. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27657051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 1 deacetylase: a key regulator of hepatic lipid metabolism.Vitam Horm. 2013;91:385-404. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407766-9.00016-X. Vitam Horm. 2013. PMID: 23374725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental Enteric Dysfunction Is Associated With Altered Bile Acid Metabolism.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017 Apr;64(4):536-540. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001313. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27322559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vlahcevic Z. R., Heuman D. M., Hylemon P. B. 1996. Physiology and pathophysiology of enterohepatic circulation of bike acids. Zakim D., Boyer T. D., editors W. B. Sanders Co., Philadelphia, PA: 376–417
-
- Makishima M., Okamoto A. Y., Repa J. J., Tu H., Learned R. M., Luk A., Hull M. V., Lustig K. D., Mangelsdorf D. J., Shan B. 1999. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science. 284: 1362–1365 - PubMed
-
- Parks D. J., Blanchard S. G., Bledsoe R. K., Chandra G., Consler T. G., Kliewer S. A., Stimmel J. B., Wilson T. M., Zavacki A. M., Moore D. D., et al. 1999. Bile acids: natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science. 284: 1365–1368 - PubMed
-
- Wang H., Chen J., Hollister K., Sowers L. C., Forman B. M. 1999. Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol. Cell. 3: 543–553 - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre P., Cariou B., Lien F., Kuipers F., Staels B. 2009. Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in metabolic regulation. Physiol. Rev. 89: 147–191 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

