A Nurr1/CoREST pathway in microglia and astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced death
- PMID: 19345186
- PMCID: PMC2754279
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.038
A Nurr1/CoREST pathway in microglia and astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced death
Abstract
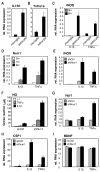
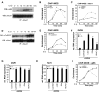
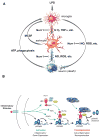
Nurr1, an orphan nuclear receptor, plays an essential role in the generation and maintenance of dopaminergic neurons in the brain. Rare mutations in Nurr1 are associated with familial Parkinson's disease, but the underlying basis for this relationship has not been established. Here, we demonstrate that Nurr1 unexpectedly functions to inhibit expression of pro-inflammatory neurotoxic mediators in both microglia and astrocytes. Reduced Nurr1 expression results in exaggerated inflammatory responses in microglia that are further amplified by astrocytes, leading to the production of factors that cause death of tyrosine hydroxylase-expressing neurons. Nurr1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects by docking to NF-kappaB-p65 on target inflammatory gene promoters in a signal-dependent manner. Subsequently, Nurr1 recruits the CoREST corepressor complex, resulting in clearance of NF-kappaB-p65 and transcriptional repression. These studies suggest that Nurr1 protects against loss of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease in part by limiting the production of neurotoxic mediators by microglia and astrocytes.
Figures
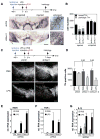
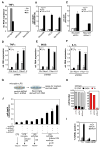
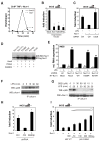
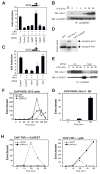
Comment in
-
A Nurr1 pathway for neuroprotection.Cell. 2009 Apr 3;137(1):26-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.024. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19345183
Similar articles
-
The Nurr1 Activator 1,1-Bis(3'-Indolyl)-1-(p-Chlorophenyl)Methane Blocks Inflammatory Gene Expression in BV-2 Microglial Cells by Inhibiting Nuclear Factor κB.Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;87(6):1021-34. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.095398. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Mol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25858541 Free PMC article.
-
A Nurr1 pathway for neuroprotection.Cell. 2009 Apr 3;137(1):26-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.024. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19345183
-
Nigrostriatal innervation is preserved in Nurr1-null mice, although dopaminergic neuron precursors are arrested from terminal differentiation.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000 Dec 8;84(1-2):67-78. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(00)00211-4. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11113533
-
The role of Nurr1 in the development of dopaminergic neurons and Parkinson's disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2005 Sep-Oct;77(1-2):128-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.09.001. Epub 2005 Oct 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16243425 Review.
-
Advances in NURR1-Regulated Neuroinflammation Associated with Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 19;23(24):16184. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416184. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory Disequilibrium in Stroke.Circ Res. 2016 Jun 24;119(1):142-58. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308022. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27340273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astroglial NF-κB mediates oxidative stress by regulation of NADPH oxidase in a model of retinal ischemia reperfusion injury.J Neurochem. 2012 Feb;120(4):586-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07595.x. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22118627 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor NR4A2 orchestrates Th17 cell-mediated autoimmune inflammation via IL-21 signalling.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056595. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437182 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid Beta, TNFα and FAIM-L; Approaching New Therapeutic Strategies for AD.Front Neurol. 2014 Dec 18;5:276. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2014.00276. eCollection 2014. Front Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25566181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Gas1 up-regulation is inducible and contributes to cell apoptosis in reactive astrocytes in the substantia nigra of LPS and MPTP models.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Jul 8;13(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0643-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27391369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarnisalo P, Kim CH, Lee JW, Perlmann T. Defining requirements for heterodimerization between the retinoid X receptor and the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35118–35123. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson TJ. Toll-like receptors, transduction-effector pathways, and disease diversity: evidence of an immunobiological paradigm explaining all human illness? Int Rev Immunol. 2008;27:255–281. - PubMed
-
- Ballas N, Grunseich C, Lu DD, Speh JC, Mandel G. REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell. 2005;121:645–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL088129/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477-34/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088129-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA052599-19/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- DK39949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059694-10/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934-19/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA052599-17/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949-27/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA052599-18/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS34934/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA052599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK1877/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034934-20A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA52599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

