SH3 domains of Grb2 adaptor bind to PXpsiPXR motifs within the Sos1 nucleotide exchange factor in a discriminate manner
- PMID: 19323566
- PMCID: PMC2710136
- DOI: 10.1021/bi802291y
SH3 domains of Grb2 adaptor bind to PXpsiPXR motifs within the Sos1 nucleotide exchange factor in a discriminate manner
Abstract
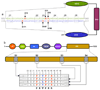
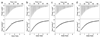
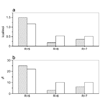
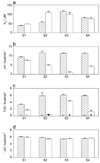
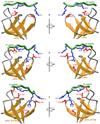
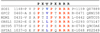
Ubiquitously encountered in a wide variety of cellular processes, the Grb2-Sos1 interaction is mediated through the combinatorial binding of nSH3 and cSH3 domains of Grb2 to various sites containing PXpsiPXR motifs within Sos1. Here, using isothermal titration calorimetry, we demonstrate that while the nSH3 domain binds with affinities in the physiological range to all four sites containing PXpsiPXR motifs, designated S1, S2, S3, and S4, the cSH3 domain can only do so at the S1 site. Further scrutiny of these sites yields rationale for the recognition of various PXpsiPXR motifs by the SH3 domains in a discriminate manner. Unlike the PXpsiPXR motifs at S2, S3, and S4 sites, the PXpsiPXR motif at the S1 site is flanked at its C-terminus with two additional arginine residues that are absolutely required for high-affinity binding of the cSH3 domain. In striking contrast, these two additional arginine residues augment the binding of the nSH3 domain to the S1 site, but their role is not critical for the recognition of S2, S3, and S4 sites. Site-directed mutagenesis suggests that the two additional arginine residues flanking the PXpsiPXR motif at the S1 site contribute to free energy of binding via the formation of salt bridges with specific acidic residues in SH3 domains. Molecular modeling is employed to project these novel findings into the 3D structures of SH3 domains in complex with a peptide containing the PXpsiPXR motif and flanking arginine residues at the S1 site. Taken together, this study furthers our understanding of the assembly of a key signaling complex central to cellular machinery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural basis of the differential binding of the SH3 domains of Grb2 adaptor to the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Sos1.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008 Nov 1;479(1):52-62. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.08.012. Epub 2008 Aug 26. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008. PMID: 18778683
-
High-Affinity Interactions of the nSH3/cSH3 Domains of Grb2 with the C-Terminal Proline-Rich Domain of SOS1.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Feb 19;142(7):3401-3411. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b10710. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 31970984 Free PMC article.
-
Multivalent binding and facilitated diffusion account for the formation of the Grb2-Sos1 signaling complex in a cooperative manner.Biochemistry. 2012 Mar 13;51(10):2122-35. doi: 10.1021/bi3000534. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22360309 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Grb2 in Cancer and Peptides as Grb2 Antagonists.Protein Pept Lett. 2018 Feb 8;24(12):1084-1095. doi: 10.2174/0929866525666171123213148. Protein Pept Lett. 2018. PMID: 29173143 Review.
-
The tandem β-zipper: modular binding of tandem domains and linear motifs.FEBS Lett. 2013 Apr 17;587(8):1164-71. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Jan 16. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23333654 Review.
Cited by
-
Regions outside of conserved PxxPxR motifs drive the high affinity interaction of GRB2 with SH3 domain ligands.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1853(10 Pt A):2560-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26079855 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying intramolecular binding in multivalent interactions: a structure-based synergistic study on Grb2-Sos1 complex.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002192. Epub 2011 Oct 13. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 22022247 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling and simulation of aggregation of membrane protein LAT with molecular variability in the number of binding sites for cytosolic Grb2-SOS1-Grb2.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e28758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028758. Epub 2012 Mar 1. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22396725 Free PMC article.
-
Application of ring-closing metathesis to Grb2 SH3 domain-binding peptides.Biopolymers. 2011;96(6):780-8. doi: 10.1002/bip.21692. Biopolymers. 2011. PMID: 21830199 Free PMC article.
-
The proline-rich region of 18.5 kDa myelin basic protein binds to the SH3-domain of Fyn tyrosine kinase with the aid of an upstream segment to form a dynamic complex in vitro.Biosci Rep. 2014 Dec 8;34(6):e00157. doi: 10.1042/BSR20140149. Biosci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25343306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chardin P, Cussac D, Maignan S, Ducruix A. The Grb2 adaptor. FEBS Lett. 1995;369:47–51. - PubMed
-
- Nimnual A, Bar-Sagi D. The two hats of SOS. Sci STKE. 2002;2002:PE36. - PubMed
-
- Li N, Batzer A, Daly R, Yajnik V, Skolnik E, Chardin P, Bar-Sagi D, Margolis B, Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993;363:85–88. - PubMed
-
- Gale NW, Kaplan S, Lowenstein EJ, Schlessinger J, Bar-Sagi D. Grb2 mediates the EGF-dependent activation of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ras. Nature. 1993;363:88–92. - PubMed
-
- Rozakis-Adcock M, McGlade J, Mbamalu G, Pelicci G, Daly R, Li W, Batzer A, Thoma S, Brugge J, Pelicci PG, Schlessinger J, Pawson T. Association of the Shc and Grb2/Sem5 SH2-containing proteins is implicated in activation of the ras pathway by tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1992;360:689–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

