Endothelium-dependent cerebral artery dilation mediated by TRPA1 and Ca2+-Activated K+ channels
- PMID: 19299646
- PMCID: PMC2966339
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.189530
Endothelium-dependent cerebral artery dilation mediated by TRPA1 and Ca2+-Activated K+ channels
Abstract
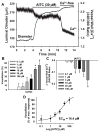
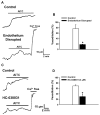
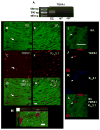
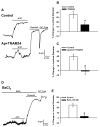
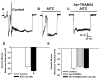
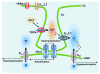
Although it is well established that changes in endothelial intracellular [Ca(2+)] regulate endothelium-dependent vasodilatory pathways, the molecular identities of the ion channels responsible for Ca(2+) influx in these cells are not clearly defined. The sole member of the ankyrin (A) transient receptor potential (TRP) subfamily, TRPA1, is a Ca(2+)-permeable nonselective cation channel activated by electrophilic compounds such as acrolein (tear gas), allicin (garlic), and allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) (mustard oil). The present study examines the hypothesis that Ca(2+) influx via TRPA1 causes endothelium-dependent vasodilation. The effects of TRPA1 activity on vascular tone were examined using isolated, pressurized cerebral arteries. AITC induced concentration-dependent dilation of pressurized vessels with myogenic tone that was accompanied by a corresponding decrease in smooth muscle intracellular [Ca(2+)]. AITC-induced dilation was attenuated by disruption of the endothelium and when the TRPA1 channel blocker HC-030031 was present in the arterial lumen. TRPA1 channels were found to be present in native endothelial cells, localized to endothelial cell membrane projections proximal to vascular smooth muscle cells. AITC-induced dilation was insensitive to nitric oxide synthase or cyclooxygenase inhibition but was blocked by luminal administration of the small and intermediate conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel blockers apamin and TRAM34. BaCl(2), a blocker of inwardly rectifying K(+) channels, also inhibited AITC-induced dilation. AITC-induced smooth muscle cell hyperpolarization was blocked by apamin and TRAM34. We conclude that Ca(2+) influx via endothelial TRPA1 channels elicits vasodilation of cerebral arteries by a mechanism involving endothelial cell Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels and inwardly rectifying K(+) channels in arterial myocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A dietary agonist of transient receptor potential cation channel V3 elicits endothelium-dependent vasodilation.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;77(4):612-20. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.060715. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20086034 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of TRPA1 activator allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) on rat dural and pial arteries.Pharmacol Rep. 2019 Aug;71(4):565-572. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2019.02.015. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Pharmacol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31132686
-
Endothelium-dependent cerebral artery dilation mediated by transient receptor potential and Ca2+-activated K+ channels.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;57(2):148-53. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181f580d9. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20729757 Review.
-
Novel role of endothelial BKCa channels in altered vasoreactivity following hypoxia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Nov;299(5):H1439-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00124.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20817829 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-activated potassium channels and endothelial dysfunction: therapeutic options?Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;156(4):545-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00052.x. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19187341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transient receptor potential channels in the vasculature.Physiol Rev. 2015 Apr;95(2):645-90. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2014. Physiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25834234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial control of vasodilation: integration of myoendothelial microdomain signalling and modulation by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Mar;466(3):389-405. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1303-3. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 23748495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of Novel TRPA1 Agonists Based on Structure of Natural Vasodilator Carvacrol-In Vitro and In Silico Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 18;16(7):951. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070951. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065648 Free PMC article.
-
TRPA1 contributes to the acute inflammatory response and mediates carrageenan-induced paw edema in the mouse.Sci Rep. 2012;2:380. doi: 10.1038/srep00380. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22532928 Free PMC article.
-
Human Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Channel: Structure, Function, and Physiology.Subcell Biochem. 2024;104:207-244. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-58843-3_10. Subcell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38963489 Review.
References
-
- Taylor MS, Bonev AD, Gross TP, Eckman DM, Brayden JE, Bond CT, Adelman JP, Nelson MT. Altered expression of small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (SK3) channels modulates arterial tone and blood pressure. Circ Res. 2003;93:124–131. - PubMed
-
- Edwards G, Dora KA, Gardener MJ, Garland CJ, Weston AH. K+ is an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in rat arteries. Nature. 1998;396:269–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

