Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human blood
- PMID: 19299331
- PMCID: PMC2689048
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-204800
Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human blood
Abstract
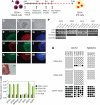
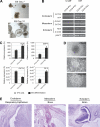
Human dermal fibroblasts obtained by skin biopsy can be reprogrammed directly to pluripotency by the ectopic expression of defined transcription factors. Here, we describe the derivation of induced pluripotent stem cells from CD34+ mobilized human peripheral blood cells using retroviral transduction of OCT4/SOX2/KLF4/MYC. Blood-derived human induced pluripotent stem cells are indistinguishable from human embryonic stem cells with respect to morphology, expression of surface antigens, and pluripotency-associated transcription factors, DNA methylation status at pluripotent cell-specific genes, and the capacity to differentiate in vitro and in teratomas. The ability to reprogram cells from human blood will allow the generation of patient-specific stem cells for diseases in which the disease-causing somatic mutations are restricted to cells of the hematopoietic lineage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficient induction of pluripotent stem cells from menstrual blood.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Apr 1;22(7):1147-58. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0428. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23151296
-
Generation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells.Nat Protoc. 2008;3(7):1180-6. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.92. Nat Protoc. 2008. PMID: 18600223
-
Generation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells from gut mesentery-derived cells by ectopic expression of OCT4/SOX2/NANOG.Cell Reprogram. 2010 Jun;12(3):237-47. doi: 10.1089/cell.2009.0103. Cell Reprogram. 2010. PMID: 20698766
-
[Generation and application of pluripotent stem cells from spermatogonial stem cells].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Feb;28(1):208-12. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21485215 Review. Chinese.
-
Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells.Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(8):1015-22. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.082640eg. Int J Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18956334 Review.
Cited by
-
Duplication Versus Deletion Through the Lens of 15q13.3: Clinical and Research Implications of Studying Copy Number Variants Associated with Neuropsychiatric Disorders in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Apr;19(3):639-650. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10475-0. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 36370261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Betwixt Mine Eye and Heart a League Is Took": The Progress of Induced Pluripotent Stem-Cell-Based Models of Dystrophin-Associated Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 23;21(19):6997. doi: 10.3390/ijms21196997. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32977524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delineating nuclear reprogramming.Protein Cell. 2012 May;3(5):329-45. doi: 10.1007/s13238-012-2920-x. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Protein Cell. 2012. PMID: 22467264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promise and challenges of human iPSC-based hematologic disease modeling and treatment.Int J Hematol. 2012 Jun;95(6):601-9. doi: 10.1007/s12185-012-1095-9. Epub 2012 May 23. Int J Hematol. 2012. PMID: 22619021 Review.
-
Cellular reprogramming: a novel tool for investigating autism spectrum disorders.Trends Mol Med. 2012 Aug;18(8):463-71. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2012.06.002. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Trends Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22771169 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
-
- Park IH, Zhao R, West JA, et al. Reprogramming of human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature. 2008;451:141–146. - PubMed
-
- Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, et al. Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:1276–1284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

