TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq
- PMID: 19289445
- PMCID: PMC2672628
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120
TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq
Abstract
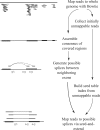
Motivation: A new protocol for sequencing the messenger RNA in a cell, known as RNA-Seq, generates millions of short sequence fragments in a single run. These fragments, or 'reads', can be used to measure levels of gene expression and to identify novel splice variants of genes. However, current software for aligning RNA-Seq data to a genome relies on known splice junctions and cannot identify novel ones. TopHat is an efficient read-mapping algorithm designed to align reads from an RNA-Seq experiment to a reference genome without relying on known splice sites.
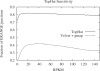
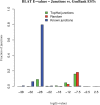
Results: We mapped the RNA-Seq reads from a recent mammalian RNA-Seq experiment and recovered more than 72% of the splice junctions reported by the annotation-based software from that study, along with nearly 20,000 previously unreported junctions. The TopHat pipeline is much faster than previous systems, mapping nearly 2.2 million reads per CPU hour, which is sufficient to process an entire RNA-Seq experiment in less than a day on a standard desktop computer. We describe several challenges unique to ab initio splice site discovery from RNA-Seq reads that will require further algorithm development.
Availability: TopHat is free, open-source software available from http://tophat.cbcb.umd.edu.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures


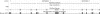
Similar articles
-
Read-Split-Run: an improved bioinformatics pipeline for identification of genome-wide non-canonical spliced regions using RNA-Seq data.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 22;17 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):503. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2896-7. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27556805 Free PMC article.
-
MapSplice: accurate mapping of RNA-seq reads for splice junction discovery.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(18):e178. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq622. Epub 2010 Aug 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20802226 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of RNA-Seq alignment algorithms and the RNA-Seq unified mapper (RUM).Bioinformatics. 2011 Sep 15;27(18):2518-28. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr427. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21775302 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping RNA-seq Reads with STAR.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 3;51:11.14.1-11.14.19. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1114s51. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26334920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocol for transcriptome assembly by the TransBorrow algorithm.Biol Methods Protoc. 2023 Nov 1;8(1):bpad028. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpad028. eCollection 2023. Biol Methods Protoc. 2023. PMID: 38023349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
What lies behind the large genome of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum.Front Fungal Biol. 2024 Oct 15;5:1459229. doi: 10.3389/ffunb.2024.1459229. eCollection 2024. Front Fungal Biol. 2024. PMID: 39473581 Free PMC article.
-
The blue light signaling inhibitor 3-bromo-7-nitroindazole affects gene translation at the initial reception of blue light in young Arabidopsis seedlings.Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2024 Jun 25;41(2):153-157. doi: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.24.0323a. Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 39463773 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Polydeoxyribonucleotides on the Morphology, Viability, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Gingiva-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Oct 1;60(10):1610. doi: 10.3390/medicina60101610. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39459397 Free PMC article.
-
AtC3H3, an Arabidopsis Non-TZF Gene, Enhances Salt Tolerance by Increasing the Expression of Both ABA-Dependent and -Independent Stress-Responsive Genes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10943. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010943. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456724 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation impacts androgen receptor signaling in basal prostate stem cells through interleukin 1 receptor antagonist.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 25;7(1):1390. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07071-y. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39455902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abouelhoda M, et al. Replacing suffix trees with enhanced suffix arrays. J. Discrete Alg. 2004;2:53–86.
-
- Adams MD, et al. Rapid cDNA sequencing (expressed sequence tags) from a directionally cloned human infant brain cDNA library. Nat. Genet. 1993;4:373–380. - PubMed
-
- Burrows M, Wheeler D. Technical Report 124. Palo Alto, California: DEC, Digital Systems Research Center; 1994. A block sorting lossless data compression algorithm.
-
- Cloonan N, et al. Stem cell transcriptome profiling via massive-scale mRNA sequencing. Nat. Meth. 2008;5:613–619. - PubMed
-
- De Bona F, et al. Optimal spliced alignments of short sequence reads. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:i174–i180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

