Thymus-homing peripheral dendritic cells constitute two of the three major subsets of dendritic cells in the steady-state thymus
- PMID: 19273629
- PMCID: PMC2699131
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20082232
Thymus-homing peripheral dendritic cells constitute two of the three major subsets of dendritic cells in the steady-state thymus
Abstract
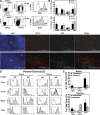
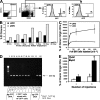
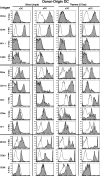
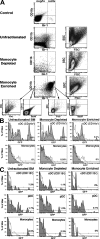
Many dendritic cells (DCs) in the normal mouse thymus are generated intrathymically from common T cell/DC progenitors. However, our previous work suggested that at least 50% of thymic DCs originate independently of these progenitors. We now formally demonstrate by parabiotic, adoptive transfer, and developmental studies that two of the three major subsets of thymic DCs originate extrathymically and continually migrate to the thymus, where they occupy a finite number of microenvironmental niches. The thymus-homing DCs consisted of immature plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) and the signal regulatory protein alpha-positive (Sirpalpha(+)) CD11b(+) CD8alpha(-) subset of conventional DCs (cDCs), both of which could take up and transport circulating antigen to the thymus. The cDCs of intrathymic origin were mostly Sirpalpha(-) CD11b(-) CD8alpha(hi) cells. Upon arrival in the thymus, the migrant pDCs enlarged and up-regulated CD11c, major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II), and CD8alpha, but maintained their plasmacytoid morphology. In contrast, the migrant cDCs proliferated extensively, up-regulated CD11c, MHC II, and CD86, and expressed dendritic processes. The possible functional implications of these findings are discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two developmentally distinct populations of dendritic cells inhabit the adult mouse thymus: demonstration by differential importation of hematogenous precursors under steady state conditions.J Immunol. 2003 Apr 1;170(7):3514-21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.7.3514. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12646612
-
Crucial contribution of thymic Sirp alpha+ conventional dendritic cells to central tolerance against blood-borne antigens in a CCR2-dependent manner.J Immunol. 2009 Sep 1;183(5):3053-63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900438. Epub 2009 Aug 12. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19675159
-
Functional redundancy between thymic CD8α+ and Sirpα+ conventional dendritic cells in presentation of blood-derived lysozyme by MHC class II proteins.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 1;186(3):1421-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002587. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21178002 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of circulating dendritic cells on the development and differentiation of thymocytes.Immunol Cell Biol. 2009 Jan;87(1):39-45. doi: 10.1038/icb.2008.86. Epub 2008 Dec 2. Immunol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19048018 Review.
-
Thymic dendritic cells: phenotype and function.Int Rev Immunol. 1990;6(2-3):187-96. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056629. Int Rev Immunol. 1990. PMID: 2152502 Review.
Cited by
-
Medullary thymic epithelial cells and CD8α+ dendritic cells coordinately regulate central tolerance but CD8α+ cells are dispensable for thymic regulatory T cell production.J Autoimmun. 2016 Dec;75:141-149. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.08.002. Epub 2016 Aug 16. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 27543048 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial and dendritic cells in the thymic medulla promote CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell development via the CD27-CD70 pathway.J Exp Med. 2013 Apr 8;210(4):715-28. doi: 10.1084/jem.20112061. Epub 2013 Apr 1. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23547099 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal increase in thymocyte negative selection parallels enhanced thymic SIRPα+ DC function.Eur J Immunol. 2016 Oct;46(10):2352-2362. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646354. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27501268 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal human thymic profiling reveals trajectories and cellular milieu for T agonist selection.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 20;13:1092028. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1092028. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36741401 Free PMC article.
-
T-Cell Receptor/HLA Humanized Mice Reveal Reduced Tolerance and Increased Immunogenicity of Posttranslationally Modified GAD65 Epitope.Diabetes. 2022 May 1;71(5):1012-1022. doi: 10.2337/db21-0993. Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35179565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu L., Shortman K. 2005. Heterogeneity of thymic dendritic cells.Semin. Immunol. 17:304–312 - PubMed
-
- Donskoy E., Goldschneider I. 2003. Two developmentally distinct populations of dendritic cells inhabit the adult mouse thymus: demonstration by differential importation of hematogenous precursors under steady state conditions.J. Immunol. 170:3514–3521 - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Goldschneider I., Foss D., Wu D.Y., O'Rourke J., Cone R.E. 1997. Direct thymic involvement in anterior chamber-associated immune deviation: evidence for a nondeletional mechanism of centrally induced tolerance to extrathymic antigens in adult mice.J. Immunol. 158:2150–2155 - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Goldschneider I., O'Rourke J., Cone R.E. 2001. Blood mononuclear cells induce regulatory NK T thymocytes in anterior chamber-associated immune deviation.J. Leukoc. Biol. 69:741–746 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

