Prostaglandin E2 regulates Th17 cell differentiation and function through cyclic AMP and EP2/EP4 receptor signaling
- PMID: 19273625
- PMCID: PMC2699124
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20082293
Prostaglandin E2 regulates Th17 cell differentiation and function through cyclic AMP and EP2/EP4 receptor signaling
Abstract
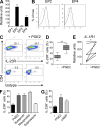
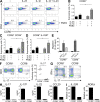
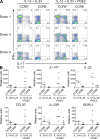
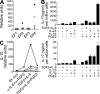
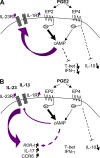
Prostaglandins, particularly prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), play an important role during inflammation. This is exemplified by the clinical use of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors, which interfere with PGE2 synthesis, as effective antiinflammatory drugs. Here, we show that PGE2 directly promotes differentiation and proinflammatory functions of human and murine IL-17-producing T helper (Th17) cells. In human purified naive T cells, PGE2 acts via prostaglandin receptor EP2- and EP4-mediated signaling and cyclic AMP pathways to up-regulate IL-23 and IL-1 receptor expression. Furthermore, PGE2 synergizes with IL-1beta and IL-23 to drive retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor (ROR)-gammat, IL-17, IL-17F, CCL20, and CCR6 expression, which is consistent with the reported Th17 phenotype. While enhancing Th17 cytokine expression mainly through EP2, PGE2 differentially regulates interferon (IFN)-gamma production and inhibits production of the antiinflammatory cytokine IL-10 in Th17 cells predominantly through EP4. Furthermore, PGE2 is required for IL-17 production in the presence of antigen-presenting cells. Hence, the combination of inflammatory cytokines and noncytokine immunomodulators, such as PGE2, during differentiation and activation determines the ultimate phenotype of Th17 cells. These findings, together with the altered IL-12/IL-23 balance induced by PGE2 in dendritic cells, further highlight the crucial role of the inflammatory microenvironment in Th17 cell development and regulation.
Figures

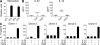
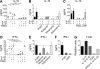

Similar articles
-
T cell-intrinsic prostaglandin E2-EP2/EP4 signaling is critical in pathogenic TH17 cell-driven inflammation.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Feb;143(2):631-643. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.05.036. Epub 2018 Jun 20. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 29935220 Free PMC article.
-
Binary regulation of interleukin (IL)-6 production by EP1 and EP2/EP4 subtypes of PGE2 receptors in IL-1beta-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts.J Periodontal Res. 2002 Feb;37(1):29-36. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0765.2002.00641.x. J Periodontal Res. 2002. PMID: 11842936
-
The IL17A and IL17F loci have divergent histone modifications and are differentially regulated by prostaglandin E2 in Th17 cells.Cytokine. 2013 Oct;64(1):404-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 Jun 22. Cytokine. 2013. PMID: 23800789 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2-induced inflammation: Relevance of prostaglandin E receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Apr;1851(4):414-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.07.008. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25038274 Review.
-
Targeting EP2 Receptor for Drug Discovery: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) Analysis.J Med Chem. 2023 Jul 27;66(14):9313-9324. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00655. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37458373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The CREB/CRTC2 pathway modulates autoimmune disease by promoting Th17 differentiation.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 2;6:7216. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8216. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26031354 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms for cAMP-Mediated Immunoregulation in T cells - Role of Anchored Protein Kinase A Signaling Units.Front Immunol. 2016 Jun 8;7:222. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00222. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27375620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung cancer: a classic example of tumor escape and progression while providing opportunities for immunological intervention.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:160724. doi: 10.1155/2012/160724. Epub 2012 Jul 29. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22899945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandin receptor EP2 in the crosshairs of anti-inflammation, anti-cancer, and neuroprotection.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Jul;34(7):413-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23796953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th1 and Th17 cells: adversaries and collaborators.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jan;1183:211-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05133.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20146717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flower R.J. 2003. The development of COX2 inhibitors.Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2:179–191 - PubMed
-
- Harris S.G., Padilla J., Koumas L., Ray D., Phipps R.P. 2002. Prostaglandins as modulators of immunity.Trends Immunol. 23:144–150 - PubMed
-
- Weaver C.T., Hatton R.D., Mangan P.R., Harrington L.E. 2007. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages.Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25:821–852 - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E., Oukka M., Kuchroo V.K. 2007. T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity.Nat. Immunol. 8:345–350 - PubMed
-
- Dong C. 2006. Diversification of T-helper-cell lineages: finding the family root of IL-17-producing cells.Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:329–333 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

