Dopamine D2 receptor levels in striatum, thalamus, substantia nigra, limbic regions, and cortex in schizophrenic subjects
- PMID: 19251247
- PMCID: PMC2951678
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.12.029
Dopamine D2 receptor levels in striatum, thalamus, substantia nigra, limbic regions, and cortex in schizophrenic subjects
Abstract
Background: Studies in schizophrenic patients have reported dopaminergic abnormalities in striatum, substantia nigra, thalamus, anterior cingulate, hippocampus, and cortex that have been related to positive symptoms and cognitive impairments.
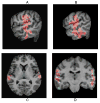
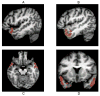
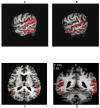
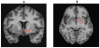
Methods: [(18)F]fallypride positron emission tomography studies were performed in off-medication or never-medicated schizophrenic subjects (n = 11, 6 men, 5 women; mean age of 30.5 +/- 8.0 [SD] years; 4 drug-naive) and age-matched healthy subjects (n = 11, 5 men, 6 women, mean age of 31.6 +/- 9.2 [SD]) to examine dopamine D(2) receptor (DA D(2)r) levels in the caudate, putamen, ventral striatum, medial thalamus, posterior thalamus, substantia nigra, amygdala, temporal cortex, anterior cingulate, and hippocampus.
Results: In schizophrenic subjects, increased DA D(2)r levels were seen in the substantia nigra bilaterally; decreased levels were seen in the left medial thalamus. Correlations of symptoms with ROI data demonstrated a significant correlation of disorganized thinking/nonparanoid delusions with the right temporal cortex ROI (r = .94, p = .0001), which remained significant after correction for multiple comparisons (p < .03). Correlations of symptoms with parametric images of DA D(2)r levels revealed no significant clusters of correlations with negative symptoms but significant clusters of positive correlations of total positive symptoms, delusions and bizarre behavior with the lateral and anterior temporal cortex, and hallucinations with the left ventral striatum.
Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrate abnormal DA D(2)r-mediated neurotransmission in the substantia nigra consistent with nigral dysfunction in schizophrenia and suggest that both temporal cortical and ventral striatal DA D(2)r mediate positive symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Kessler has investigator initiated research support from Janssen, consults with and is a shareholder in PharmorRx. Dr. Herbert Meltzer has been a consultant to and received grants from Abbot, ACADIA, ARYx, BioLine Rx, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cephalon, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Litmus Molecular Design, Memory, Minster, and Pfizer. Dr Meltzer has been a consultant to Astellas, Glaxo Smith Kline, Lundbeck, Merck, Otsuka, Roche, and Solvay, and has received grants from Dainippon Sumitomo, Sepreacor, and SK Pharma. Drs. Woodward, Riccardi, Dawant, and Zald, Mr. Ansari and Li, and Ms. Anderson have no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Occupancy of striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors by clozapine and quetiapine.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Sep;31(9):1991-2001. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301108. Epub 2006 May 31. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16738543
-
Amphetamine-induced displacement of [18F] fallypride in striatum and extrastriatal regions in humans.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 May;31(5):1016-26. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300916. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16237395
-
Occupancy of striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2/D3 receptors by olanzapine and haloperidol.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Dec;30(12):2283-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300836. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 16123775 Clinical Trial.
-
The role of extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors in schizophrenia.Biol Psychiatry. 2006 May 15;59(10):919-28. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.01.022. Biol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16682269 Review.
-
The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: a review.Schizophr Bull. 1976;2(1):19-76. doi: 10.1093/schbul/2.1.19. Schizophr Bull. 1976. PMID: 779020 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Modeling psychiatric disorders at the cellular and network levels.Mol Psychiatry. 2012 Dec;17(12):1239-53. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.20. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Mol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22472874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thinking outside a less intact box: thalamic dopamine D2 receptor densities are negatively related to psychometric creativity in healthy individuals.PLoS One. 2010 May 17;5(5):e10670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010670. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20498850 Free PMC article.
-
Nigrostriatal and Mesolimbic D2/3 Receptor Expression in Parkinson's Disease Patients with Compulsive Reward-Driven Behaviors.J Neurosci. 2018 Mar 28;38(13):3230-3239. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3082-17.2018. Epub 2018 Feb 26. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29483278 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of novelty seeking by midbrain dopamine D2/D3 signaling and ghrelin is altered in obesity.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014 Jun;22(6):1452-7. doi: 10.1002/oby.20690. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014. PMID: 24415718 Free PMC article.
-
Accentuated Paralimbic and Reduced Mesolimbic D2/3-Impulsivity Associations in Parkinson's Disease.J Neurosci. 2023 Dec 13;43(50):8733-8743. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1037-23.2023. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37852792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davis KL, Kahn RS, Ko G, Davidson M. Dopamine in Schizophrenia: A Review and Reconceptualization. Am J Psychiatr. 1991;148:1474–86. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger DR, Egan MF, Bertolino A, Callicott JH, Mattay VS, Lipska BK, Berman KF, Goldberg TE. Prefrontal Neurons and the Genetics of Schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;50:825–844. - PubMed
-
- Goldman-Rakic PS. The Relevance of the Dopamine-D1 Receptor in the Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21 6:S171–S177.
-
- Bilder RM, Reiter G, Bates J, Lencz T, Szeszko P, Goldman RS, Robinson D, Lieberman JA, Kane JM. Cognitive development in schizophrenia: follow-back from the first episode. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2006;28(2):270–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

