A temporal threshold for formaldehyde crosslinking and fixation
- PMID: 19247482
- PMCID: PMC2645674
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004636
A temporal threshold for formaldehyde crosslinking and fixation
Abstract
Background: Formaldehyde crosslinking is in widespread use as a biological fixative for microscopy and molecular biology. An assumption behind its use is that most biologically meaningful interactions are preserved by crosslinking, but the minimum length of time required for an interaction to become fixed has not been determined.
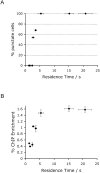
Methodology: Using a unique series of mutations in the DNA binding protein MeCP2, we show that in vivo interactions lasting less than 5 seconds are invisible in the microscope after formaldehyde fixation, though they are obvious in live cells. The stark contrast between live cell and fixed cell images illustrates hitherto unsuspected limitations to the fixation process. We show that chromatin immunoprecipitation, a technique in widespread use that depends on formaldehyde crosslinking, also fails to capture these transient interactions.
Conclusions/significance: Our findings for the first time establish a minimum temporal limitation to crosslink chemistry that has implications for many fields of research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
MeCP2 nuclear dynamics in live neurons results from low and high affinity chromatin interactions.Elife. 2019 Dec 23;8:e51449. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51449. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31868585 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of protein domains and Rett syndrome mutations indicate that multiple regions influence chromatin-binding dynamics of the chromatin-associated protein MECP2 in vivo.J Cell Sci. 2008 Apr 1;121(Pt 7):1128-37. doi: 10.1242/jcs.016865. Epub 2008 Mar 11. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 18334558 Free PMC article.
-
MeCP2 interacts with chromosomal microRNAs in brain.Epigenetics. 2017;12(12):1028-1037. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2017.1391429. Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 29412786 Free PMC article.
-
Formaldehyde crosslinking: a tool for the study of chromatin complexes.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 30;290(44):26404-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.651679. Epub 2015 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26354429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MECP2, a multi-talented modulator of chromatin architecture.Brief Funct Genomics. 2016 Nov;15(6):420-431. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elw023. Epub 2016 Jun 12. Brief Funct Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27296483 Review.
Cited by
-
Human mutations affect the epigenetic/bookmarking function of HNF1B.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 30;44(17):8097-111. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw467. Epub 2016 May 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27229139 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic nature and territory of transcriptional machinery in the bacterial chromosome.Front Microbiol. 2015 May 21;6:497. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00497. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26052320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xist localization and function: new insights from multiple levels.Genome Biol. 2015 Aug 15;16(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0733-y. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 26282267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Live-cell single particle tracking of PRC1 reveals a highly dynamic system with low target site occupancy.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 9;12(1):887. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21130-6. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33563969 Free PMC article.
-
The second decade of 3C technologies: detailed insights into nuclear organization.Genes Dev. 2016 Jun 15;30(12):1357-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.281964.116. Genes Dev. 2016. PMID: 27340173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Solomon MJ, Larsen PL, Varshavsky A. Mapping protein-DNA interactions in vivo with formaldehyde: evidence that histone H4 is retained on a highly transcribed gene. Cell. 1988;53:937–47. - PubMed
-
- Gilmour DS, Rougvie AE, Lis JT. Protein-DNA cross-linking as a means to Determine the distribution of proteins on DNA in vivo. Methods in Cell Biology. 1991;35:369–381. - PubMed
-
- Orlando V, Strutt H, Paro R. Analysis of chromatin structure by in vivo formaldehyde cross-linking. Methods. 1997;11:205–14. - PubMed
-
- Lewis JD, Meehan RR, Henzel WJ, Maurer-Fogy I, Jeppesen P, et al. Purification, sequence and cellular localisation of a novel chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA. Cell. 1992;69:905–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

