Mechanism of Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L) inhibition of NLRP1 inflammasome: loop domain-dependent suppression of ATP binding and oligomerization
- PMID: 19223583
- PMCID: PMC2656183
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0809414106
Mechanism of Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L) inhibition of NLRP1 inflammasome: loop domain-dependent suppression of ATP binding and oligomerization
Abstract
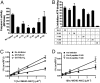
NLRP1 (NLR family, pyrin domain-containing 1) is a contributor to innate immunity involved in intracellular sensing of pathogens, as well as danger signals related to cell injury. NLRP1 is one of the core components of caspase-1-activating platforms termed "inflammasomes," which are involved in proteolytic processing of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) and in cell death. We previously discovered that anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L) bind to and inhibit NLRP1 in cells. Using an in vitro reconstituted system employing purified recombinant proteins, we studied the mechanism by which Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L) inhibit NLRP1. Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L) inhibited caspase-1 activation induced by NLRP1 in a concentration-dependent manner, with K(i) approximately 10 nM. Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L) were also determined to inhibit ATP binding to NLRP1, which is required for oligomerization of NLRP1, and Bcl-X(L) was demonstrated to interfere with NLRP1 oligomerization. Deletion of the flexible loop regions of Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L), which are located between the first and second alpha-helices of these anti-apoptotic proteins and which were previously shown to be required for binding NLRP1, abrogated ability to inhibit caspase-1 activation, ATP binding and oligomerization of NLRP1. Conversely, synthetic peptides corresponding to the loop region of Bcl-2 were sufficient to potently inhibit NLRP1. These findings thus demonstrate that the loop domain is necessary and sufficient to inhibit NLRP1, providing insights into the mechanism by which anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L) inhibit NLRP1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

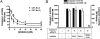
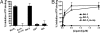


Similar articles
-
Reconstituting the NLRP1 inflammasome in vitro.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1040:137-52. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-523-1_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23852602
-
Reconstituted NALP1 inflammasome reveals two-step mechanism of caspase-1 activation.Mol Cell. 2007 Mar 9;25(5):713-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.032. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17349957
-
Cytokine Secretion and Pyroptosis of Thyroid Follicular Cells Mediated by Enhanced NLRP3, NLRP1, NLRC4, and AIM2 Inflammasomes Are Associated With Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1197. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01197. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915579 Free PMC article.
-
The NLRP1 inflammasomes.Immunol Rev. 2015 May;265(1):22-34. doi: 10.1111/imr.12283. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25879281 Review.
-
NLRP1 Inflammasomes: A Potential Target for the Treatment of Several Types of Brain Injury.Front Immunol. 2022 May 30;13:863774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.863774. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35707533 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functions of BCL-X L at the Interface between Cell Death and Metabolism.Int J Cell Biol. 2013;2013:705294. doi: 10.1155/2013/705294. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Int J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23533418 Free PMC article.
-
The mitomiR/Bcl-2 axis affects mitochondrial function and autophagic vacuole formation in senescent endothelial cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2018 Oct 21;10(10):2855-2873. doi: 10.18632/aging.101591. Aging (Albany NY). 2018. PMID: 30348904 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of rare genetic variation of NLRP1 gene in familial multiple sclerosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 16;7(1):3715. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03536-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28623311 Free PMC article.
-
Context-Dependent Regulation of Autophagy by IKK-NF-κB Signaling: Impact on the Aging Process.Int J Cell Biol. 2012;2012:849541. doi: 10.1155/2012/849541. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Int J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22899934 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin suppresses NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal death in ischemic stroke.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Sep 5;4(9):e790. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.326. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24008734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mariathasan S, Monack DM. Inflammasome adaptors and sensors: Intracellular regulators of infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Salvesen GS. Caspases and apoptosis. Essays Biochem. 2002;38:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S. Apoptosis by death factor. Cell. 1997;88:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Ting JP, Willingham SB, Bergstralh DT. NLRs at the intersection of cell death and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:372–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

