Vectors expressing efficient RNA decoys achieve the long-term suppression of specific microRNA activity in mammalian cells
- PMID: 19223327
- PMCID: PMC2665227
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp040
Vectors expressing efficient RNA decoys achieve the long-term suppression of specific microRNA activity in mammalian cells
Abstract
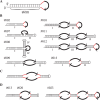
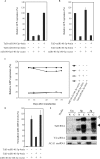
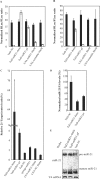
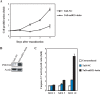
Whereas the strong and stable suppression of specific microRNA activity would be essential for the functional analysis of these molecules, and also for the development of therapeutic applications, effective inhibitory methods to achieve this have not yet been fully established. In our current study, we tested various RNA decoys which were designed to efficiently expose indigestible complementary RNAs to a specific miRNA molecule. These inhibitory RNAs were at the same time designed to be expressed in lentiviral vectors and to be transported into the cytoplasm after transcription by RNA polymerase III. We report the optimal conditions that we have established for the design of such RNA decoys (we term these molecules TuD RNAs; tough decoy RNAs). We finally demonstrate that TuD RNAs induce specific and strong biological effects and also show that TuD RNAs achieve the efficient and long-term-suppression of specific miRNAs for over 1 month in mammalian cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A potent 2'-O-methylated RNA-based microRNA inhibitor with unique secondary structures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Apr;40(8):e58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1317. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22259037 Free PMC article.
-
RNA accessibility impacts potency of Tough Decoy microRNA inhibitors.RNA Biol. 2018;15(11):1410-1419. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1537746. Epub 2018 Nov 7. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 30339041 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of microRNAs by dual-targeting and clustered Tough Decoy inhibitors.RNA Biol. 2013 Mar;10(3):406-14. doi: 10.4161/rna.23543. Epub 2013 Jan 16. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23324610 Free PMC article.
-
Lentiviral vectors for cutaneous RNA managing.Exp Dermatol. 2012 Mar;21(3):162-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2011.01436.x. Exp Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22379961 Review.
-
Signals from noncoding RNAs: unconventional roles for conventional pol III transcripts.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Nov;44(11):1847-51. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.07.013. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22819850 Review.
Cited by
-
A potent 2'-O-methylated RNA-based microRNA inhibitor with unique secondary structures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Apr;40(8):e58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1317. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22259037 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor 6 derived from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells reduces age-related functional deterioration in multiple tissues.Aging (Albany NY). 2016 Jun;8(6):1259-75. doi: 10.18632/aging.100982. Aging (Albany NY). 2016. PMID: 27311402 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of MicroRNA-34 Sponges and Tough Decoys for the Heart: Developments and Challenges.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 21;9:1090. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01090. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30298011 Free PMC article.
-
miR-140-5p Attenuates Hypoxia-Induced Breast Cancer Progression by Targeting Nrf2/HO-1 Axis in a Keap1-Independent Mechanism.Cells. 2021 Dec 22;11(1):12. doi: 10.3390/cells11010012. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011574 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs Regulating Autophagy in Neurodegeneration.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1208:191-264. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-2830-6_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34260028
References
-
- Fujita S, Ito T, Mizutani T, Minoguchi S, Yamamichi N, Sakurai K, Iba H. miR-21 Gene expression triggered by AP-1 is sustained through a double-negative feedback mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 2008;378:492–504. - PubMed
-
- Fujita S, Iba H. Putative promoter regions of miRNA genes involved in evolutionarily conserved regulatory systems among vertebrates. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Li QJ, Chau J, Ebert PJ, Sylvester G, Min H, Liu G, Braich R, Manoharan M, Soutschek J, Skare P, et al. miR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of T cell sensitivity and selection. Cell. 2007;129:147–161. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

