The inflammasome: a caspase-1-activation platform that regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis
- PMID: 19221555
- PMCID: PMC2820724
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1703
The inflammasome: a caspase-1-activation platform that regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis
Abstract
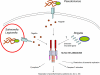
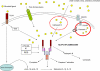
The inflammasome is a multiprotein complex that mediates the activation of caspase-1, which promotes secretion of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) and IL-18, as well as 'pyroptosis', a form of cell death induced by bacterial pathogens. Members of the Nod-like receptor family, including NLRP1, NLRP3 and NLRC4, and the adaptor ASC are critical components of the inflammasome that link microbial and endogenous 'danger' signals to caspase-1 activation. Several diseases are associated with dysregulated activation of caspase-1 and secretion of IL-1beta. Thus, understanding inflammasome pathways may provide insight into disease pathogenesis that might identify potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammasomes: guardians of cytosolic sanctity.Immunol Rev. 2009 Jan;227(1):95-105. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00730.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19120479 Review.
-
Mechanisms of NOD-like receptor-associated inflammasome activation.Immunity. 2013 Sep 19;39(3):432-41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.037. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 24054327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine Secretion and Pyroptosis of Thyroid Follicular Cells Mediated by Enhanced NLRP3, NLRP1, NLRC4, and AIM2 Inflammasomes Are Associated With Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1197. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01197. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915579 Free PMC article.
-
Uric acid induces trophoblast IL-1β production via the inflammasome: implications for the pathogenesis of preeclampsia.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2011 Jun;65(6):542-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00960.x. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21352397 Free PMC article.
-
Shiga Toxins Activate the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway To Promote Both Production of the Proinflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-1β and Apoptotic Cell Death.Infect Immun. 2015 Oct 26;84(1):172-86. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01095-15. Print 2016 Jan. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26502906 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes are essential for distinct outcomes of decreased cytokines but enhanced bacterial killing upon chronic Nod2 stimulation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 Mar 15;304(6):G583-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00297.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23287275 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of CD147 Attenuated Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Progression in an NLRP3-Dependent Manner.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 13;8:784. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00784. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32903542 Free PMC article.
-
Mice Lacking the Purinergic Receptor P2X5 Exhibit Defective Inflammasome Activation and Early Susceptibility to Listeria monocytogenes.J Immunol. 2020 Aug 1;205(3):760-766. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901423. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32540996 Free PMC article.
-
Cold-induced urticaria with a familial transmission: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2012 Feb 20;6:70. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-6-70. J Med Case Rep. 2012. PMID: 22348744 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of TLR2 worsens spontaneous colitis in MDR1A deficiency through commensally induced pyroptosis.J Immunol. 2013 Jun 1;190(11):5676-88. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201592. Epub 2013 May 1. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23636052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Ishii KJ, Koyama S, Nakagawa A, Coban C, Akira S. Host innate immune receptors and beyond: making sense of microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe. 2008;3:352–363. - PubMed
-
- Ye Z, Ting JP. NLR, the nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat containing gene family. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008;20:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Franchi L, McDonald C, Kanneganti TD, Amer A, Nunez G. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors: intracellular pattern recognition molecules for pathogen detection and host defense. J Immunol. 2006;177:3507–3513. - PubMed
-
- Franchi L, et al. Intracellular NOD-like receptors in innate immunity, infection and disease. Cell Microbiol. 2008;10:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

