Mechanotransduction gone awry
- PMID: 19197333
- PMCID: PMC2668954
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm2597
Mechanotransduction gone awry
Abstract
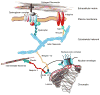
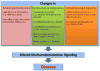
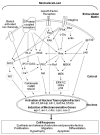
Cells sense their physical surroundings through mechanotransduction - that is, by translating mechanical forces and deformations into biochemical signals such as changes in intracellular calcium concentration or by activating diverse signalling pathways. In turn, these signals can adjust cellular and extracellular structure. This mechanosensitive feedback modulates cellular functions as diverse as migration, proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, and is crucial for organ development and homeostasis. Consequently, defects in mechanotransduction - often caused by mutations or misregulation of proteins that disturb cellular or extracellular mechanics - are implicated in the development of various diseases, ranging from muscular dystrophies and cardiomyopathies to cancer progression and metastasis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nuclear mechanics and mechanotransduction in health and disease.Curr Biol. 2013 Dec 16;23(24):R1113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.11.009. Curr Biol. 2013. PMID: 24355792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of mechanotransduction: Emerging roles for septins.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019 Jan;76(1):115-122. doi: 10.1002/cm.21485. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 30091182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium's role in mechanotransduction during muscle development.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33(2):249-72. doi: 10.1159/000356667. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24525559 Review.
-
Involvement of the FAK Network in Pathologies Related to Altered Mechanotransduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 10;21(24):9426. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249426. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33322030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanics in the nervous system: From development to disease.Neuron. 2024 Feb 7;112(3):342-361. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.10.005. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Neuron. 2024. PMID: 37967561 Review.
Cited by
-
Discriminating the Independent Influence of Cell Adhesion and Spreading Area on Stem Cell Fate Determination Using Micropatterned Surfaces.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 28;6:28708. doi: 10.1038/srep28708. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27349298 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in muscle cell metabolism and mechanotransduction are associated with myopathic phenotype in a mouse model of collagen VI deficiency.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56716. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056716. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437220 Free PMC article.
-
A high throughput cell stretch device for investigating mechanobiology in vitro.APL Bioeng. 2024 Jun 26;8(2):026129. doi: 10.1063/5.0206852. eCollection 2024 Jun. APL Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 38938688 Free PMC article.
-
Renin Cell Baroreceptor, a Nuclear Mechanotransducer Central for Homeostasis.Circ Res. 2021 Jul 9;129(2):262-276. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318711. Epub 2021 May 17. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33993729 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic strategies for preventing skeletal muscle fibrosis after injury.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Apr 21;6:87. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00087. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25954202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126:677–89. - PubMed
-
- Paszek MJ, et al. Tensional homeostasis and the malignant phenotype. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:241–54. This paper presents an elegant study linking matrix stiffness and cytoskeletal tension to cancer progression. As a component of a “mechano-regulatory circuit” that includes integrins, Rho, and ERK, disruption of tensional homeostasis can promote malignant phenotype in a model of breast cancer. - PubMed
-
- Ingber DE. Cellular mechanotransduction: putting all the pieces together again. FASEB J. 2006;20:811–27. - PubMed
-
- Orr AW, Helmke BP, Blackman BR, Schwartz MA. Mechanisms of mechanotransduction. Dev Cell. 2006;10:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Vogel V, Sheetz M. Local force and geometry sensing regulate cell functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:265–75. This is a comprehensive review of the literature on how physical cues in the microenvironment of a eukaryotic cell are sensed and converted to biochemical signals that define cell shape and regulate cell growth, differentiation, and survival. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

