MicroRNA-1 negatively regulates expression of the hypertrophy-associated calmodulin and Mef2a genes
- PMID: 19188439
- PMCID: PMC2663304
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01222-08
MicroRNA-1 negatively regulates expression of the hypertrophy-associated calmodulin and Mef2a genes
Abstract
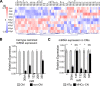
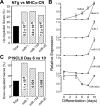
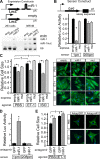
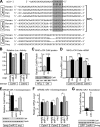
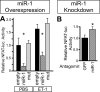
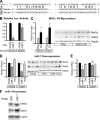
Calcium signaling is a central regulator of cardiomyocyte growth and function. Calmodulin is a critical mediator of calcium signals. Because the amount of calmodulin within cardiomyocytes is limiting, the precise control of calmodulin expression is important for the regulation of calcium signaling. In this study, we show for the first time that calmodulin levels are regulated posttranscriptionally in heart failure. The cardiomyocyte-restricted microRNA miR-1 inhibited the translation of calmodulin-encoding mRNAs via highly conserved target sites within their 3' untranslated regions. In keeping with its effect on calmodulin expression, miR-1 downregulated calcium-calmodulin signaling through calcineurin to NFAT. miR-1 also negatively regulated the expression of Mef2a and Gata4, key transcription factors that mediate calcium-dependent changes in gene expression. Consistent with the downregulation of these hypertrophy-associated genes, miR-1 attenuated cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and in the intact adult heart. Our data indicate that miR-1 regulates cardiomyocyte growth responses by negatively regulating the calcium signaling components calmodulin, Mef2a, and Gata4.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GATA4 expression is primarily regulated via a miR-26b-dependent post-transcriptional mechanism during cardiac hypertrophy.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Mar 15;93(4):645-54. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs001. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22219180 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-26a protects against cardiac hypertrophy via inhibiting GATA4 in rat model and cultured cardiomyocytes.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Sep;14(3):2860-6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5574. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27485101
-
Transcriptional upregulation of calcineurin Abeta by endothelin-1 is partially mediated by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIdelta3 in rat cardiomyocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 May-Jun;1799(5-6):429-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.02.004. Epub 2010 Mar 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20215061
-
Regulation of Cardiac Transcription Factor GATA4 by Post-Translational Modification in Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy and Heart Failure.Int Heart J. 2016 Dec 2;57(6):672-675. doi: 10.1536/ihj.16-404. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Int Heart J. 2016. PMID: 27818483 Review.
-
Calcium-regulated transcriptional pathways in the normal and pathologic heart.IUBMB Life. 2011 Oct;63(10):847-55. doi: 10.1002/iub.545. Epub 2011 Sep 7. IUBMB Life. 2011. PMID: 21901815 Review.
Cited by
-
Antisense MicroRNA Therapeutics in Cardiovascular Disease: Quo Vadis?Mol Ther. 2015 Dec;23(12):1810-8. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.133. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Mol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26216517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA-based diagnostics and therapy in cardiovascular disease-Summing up the facts.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2015 Feb;5(1):17-36. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-3652.2014.12.03. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2015. PMID: 25774345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF-1 deficiency resists cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial contractile dysfunction: role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133a.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Jan;16(1):83-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01307.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21418519 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs Association in the Cardiac Hypertrophy Secondary to Complex Congenital Heart Disease in Children.Pediatr Cardiol. 2017 Jun;38(5):991-1003. doi: 10.1007/s00246-017-1607-8. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Pediatr Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28382463
-
FoxP1 Represses MEF2A in Striated Muscle.Mol Cell Biol. 2024;44(2):57-71. doi: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2323959. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38483114
References
-
- Bartel, D. P. 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116281-297. - PubMed
-
- Betel, D., M. Wilson, A. Gabow, D. S. Marks, and C. Sander. 2008. The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 36D149-D153. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bisping, E., S. Ikeda, S. W. Kong, O. Tarnavski, N. Bodyak, J. R. McMullen, S. Rajagopal, J. K. Son, Q. Ma, Z. Springer, P. M. Kang, S. Izumo, and W. T. Pu. 2006. Gata4 is required for maintenance of postnatal cardiac function and protection from pressure overload-induced heart failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 10314471-14476. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
