Bradykinin-induced astrocyte-neuron signalling: glutamate release is mediated by ROS-activated volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channels
- PMID: 19188250
- PMCID: PMC2697293
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.165084
Bradykinin-induced astrocyte-neuron signalling: glutamate release is mediated by ROS-activated volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channels
Abstract
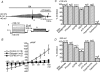
Glial cells release gliotransmitters which signal to adjacent neurons and glial cells. Previous studies showed that in response to stimulation with bradykinin, glutamate is released from rat astrocytes and causes NMDA receptor-mediated elevation of intracellular Ca(2+) in adjacent neurons. Here, we investigate how bradykinin-induced glutamate release from mouse astrocytes signals to neighbouring neurons in co-cultures. Astrocyte-to-neuron signalling and bradykinin-induced glutamate release from mouse astrocytes were both inhibited by the anion channel blocker 4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid (DIDS) and phloretin. Glutamate release was also sensitive to 4-(2-Butyl-6,7-dichlor-2-cyclopentylindan-1-on-5-yl) oxybutyric acid (DCPIB), a specific blocker of the volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channel (VSOR). Astrocytes, but not neurons, responded to bradykinin with activation of whole-cell Cl- currents. Although astrocytes stimulated with bradykinin did not undergo cell swelling, the bradykinin-activated current exhibited properties typical of VSOR: outward rectification, inhibition by osmotic shrinkage, sensitivity to DIDS, phloretin and DCPIB, dependence on intracellular ATP, and permeability to glutamate. Bradykinin increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in mouse astrocytes. Pretreatment of mouse astrocytes with either a ROS scavenger or an NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitor blocked bradykinin-induced activation of VSOR, glutamate release and astrocyte-to-neuron signalling. By contrast, pretreatment with BAPTA-AM or tetanus neurotoxin A failed to suppress bradykinin-induced glutamate release. Thus, VSOR activated by ROS in mouse astrocytes in response to stimulation with bradykinin, serves as the pathway for glutamate release to mediate astrocyte-to-neuron signalling. Since bradykinin is an initial mediator of inflammation, VSOR might play a role in glia-neuron communication in the brain during inflammation.
Figures

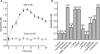
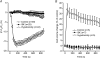
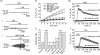
Similar articles
-
Glutamate-mediated astrocyte-neuron signalling.Nature. 1994 Jun 30;369(6483):744-7. doi: 10.1038/369744a0. Nature. 1994. PMID: 7911978
-
Roles of two types of anion channels in glutamate release from mouse astrocytes under ischemic or osmotic stress.Glia. 2006 Oct;54(5):343-57. doi: 10.1002/glia.20400. Glia. 2006. PMID: 16883573
-
Activation of volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying chloride channel by ROS contributes to ER stress and cardiac contractile dysfunction: involvement of CHOP through Wnt.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Nov 20;5(11):e1528. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.479. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25412307 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of volume-regulatory anion channels, VSOR and Maxi-Cl, in apoptosis, cisplatin resistance, necrosis, ischemic cell death, stroke and myocardial infarction.Curr Top Membr. 2019;83:205-283. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Curr Top Membr. 2019. PMID: 31196606 Review.
-
Pathophysiology and puzzles of the volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channel.J Physiol. 2009 May 15;587(Pt 10):2141-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.165076. Epub 2009 Jan 26. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19171657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Bradykinin Postconditioning on Ischemic and Toxic Brain Damage.Neurochem Res. 2015 Aug;40(8):1728-38. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1675-1. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 26216051 Free PMC article.
-
Turning down the volume: Astrocyte volume change in the generation and termination of epileptic seizures.Neurobiol Dis. 2017 Aug;104:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.04.016. Epub 2017 Apr 22. Neurobiol Dis. 2017. PMID: 28438505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The properties, functions, and pathophysiology of maxi-anion channels.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Mar;468(3):405-20. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1774-5. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26733413 Review.
-
RNA-seq and GSEA identifies suppression of ligand-gated chloride efflux channels as the major gene pathway contributing to form deprivation myopia.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 5;11(1):5280. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84338-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33674625 Free PMC article.
-
Kinin B2 Receptor Activation Prevents the Evolution of Alzheimer's Disease Pathological Characteristics in a Transgenic Mouse Model.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Oct 1;13(10):288. doi: 10.3390/ph13100288. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33019732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG. Glutamate-dependent astrocyte modulation of synaptic transmission between cultured hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:2129–2142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

