Ppp1r15 gene knockout reveals an essential role for translation initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2alpha) dephosphorylation in mammalian development
- PMID: 19181853
- PMCID: PMC2644123
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0809632106
Ppp1r15 gene knockout reveals an essential role for translation initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2alpha) dephosphorylation in mammalian development
Abstract
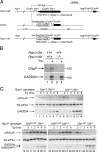
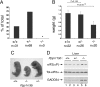
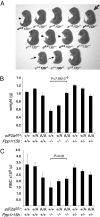
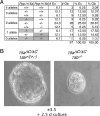
Diverse cellular stress responses are linked to phosphorylation of serine 51 on the alpha subunit of translation initiation factor 2. The resultant attenuation of protein synthesis and activation of gene expression figure heavily in the adaptive response to stress, but dephosphorylation of eIF2(alphaP), which terminates signaling in this pathway, is less well understood. GADD34 and CReP, the products of the related mammalian genes Ppp1r15a and Ppp1r15b, can recruit phosphatase catalytic subunits of the PPP1 class to eIF2(alphaP), but the significance of their contribution to its dephosphorylation has not been explored systematically. Here we report that unlike Ppp1r15a mutant mice, which are superficially indistinguishable from wild type, Ppp1r15b(-/-) mouse embryos survive gestation but exhibit severe growth retardation and impaired erythropoiesis, and loss of both Ppp1r15 genes leads to early embryonic lethality. These loss-of-function phenotypes are rescued by a mutation, Eif2a(S51A), that prevents regulated phosphorylation of eIF2alpha. These findings reveal that the essential process of eIF2(alphaP) dephosphorylation is the predominant role of PPP1R15 proteins in mammalian development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The PPP1R15 Family of eIF2-alpha Phosphatase Targeting Subunits (GADD34 and CReP).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 10;24(24):17321. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417321. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nck in a complex containing the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 regulates eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha signaling and cell survival to endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 8;281(36):26633-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M513556200. Epub 2006 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16835242
-
Substrate recruitment via eIF2γ enhances catalytic efficiency of a holophosphatase that terminates the integrated stress response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 2;121(14):e2320013121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2320013121. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38547060 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinate regulation of eIF2α phosphorylation by PPP1R15 and GCN2 is required during Drosophila development.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 15;126(Pt 6):1406-15. doi: 10.1242/jcs.117614. Epub 2013 Feb 15. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23418347 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Methods for Detecting eIF2α Phosphorylation and the Integrated Stress Response.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2428:3-18. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1975-9_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35171470 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 34 (GADD34) on inflammation-induced colon cancer in mice.Br J Cancer. 2015 Aug 11;113(4):669-79. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.263. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26196182 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating the landscape of the unfolded protein response in CD8+ T cells.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 4;15:1427859. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427859. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39026685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The extended PP1 toolkit: designed to create specificity.Trends Biochem Sci. 2010 Aug;35(8):450-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 May 1. Trends Biochem Sci. 2010. PMID: 20399103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The African swine fever virus DP71L protein recruits the protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit to dephosphorylate eIF2alpha and inhibits CHOP induction but is dispensable for these activities during virus infection.J Virol. 2010 Oct;84(20):10681-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01027-10. Epub 2010 Aug 11. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20702639 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive basal phosphorylation of eIF2α is responsible for resistance to cellular stress-induced cell death in Pten-null hepatocytes.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Dec;9(12):1708-17. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0299. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22009178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hinnebusch AG. Mechanism and regulation of initiator methionyl-tRNA binding to ribosomes. In: Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, Mathews MB, editors. Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press; 2000. pp. 185–243.
-
- Ron D, Harding H. eIF2a phosphorylation in cellular stress responses and disease. In: Sonenberg N, Hershey J, Mathews M, editors. Translational Control. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press; 2007. pp. 345–368. Cold Spring Harbor Monograph Series.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 DK042394-10/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057346/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK042394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK047119/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052173-12/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK42394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057346-100006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK042394-09/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK47119/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052173-11/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047119/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057346-11A18575/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES008681/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- ES08681/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL52173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK042394-11/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK042394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

