DAP-kinase-mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain of beclin 1 promotes dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and induction of autophagy
- PMID: 19180116
- PMCID: PMC2658558
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2008.246
DAP-kinase-mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain of beclin 1 promotes dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and induction of autophagy
Abstract
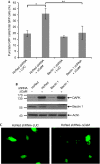
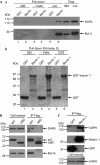
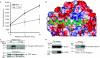
Autophagy, an evolutionarily conserved process, has functions both in cytoprotective and programmed cell death mechanisms. Beclin 1, an essential autophagic protein, was recently identified as a BH3-domain-only protein that binds to Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic family members. The dissociation of beclin 1 from its Bcl-2 inhibitors is essential for its autophagic activity, and therefore should be tightly controlled. Here, we show that death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) regulates this process. The activated form of DAPK triggers autophagy in a beclin-1-dependent manner. DAPK phosphorylates beclin 1 on Thr 119 located at a crucial position within its BH3 domain, and thus promotes the dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and the induction of autophagy. These results reveal a substrate for DAPK that acts as one of the core proteins of the autophagic machinery, and they provide a new phosphorylation-based mechanism that reduces the interaction of beclin 1 with its inhibitors to activate the autophagic machinery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
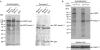
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of Beclin 1 by DAP-kinase promotes autophagy by weakening its interactions with Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL.Autophagy. 2009 Jul;5(5):720-2. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.5.8625. Epub 2009 Jul 2. Autophagy. 2009. PMID: 19395874
-
Differential interactions between Beclin 1 and Bcl-2 family members.Autophagy. 2007 Nov-Dec;3(6):561-8. doi: 10.4161/auto.4713. Epub 2007 Jul 8. Autophagy. 2007. PMID: 17643073
-
Molecular basis of Bcl-xL's target recognition versatility revealed by the structure of Bcl-xL in complex with the BH3 domain of Beclin-1.J Mol Biol. 2007 Sep 7;372(1):223-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.069. Epub 2007 Jun 30. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17659302
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Apr;18(4):571-80. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.191. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21311563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress of T cell autophagy in autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1425443. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425443. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39104538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular modulation of autophagy: New venture to target resistant cancer stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2020 May 26;12(5):303-322. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i5.303. World J Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32547680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The BECN1 N-terminal domain is intrinsically disordered.Autophagy. 2016;12(3):460-71. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1140292. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 27046249 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and functional significance of autophagy in respiratory cell biology and disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Jan;48(1):1-9. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0282TR. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 22984088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress, the unfolded protein response, autophagy, and the integrated regulation of breast cancer cell fate.Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 15;72(6):1321-31. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3213. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22422988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

