Structural determinants of integrin binding to the talin rod
- PMID: 19176533
- PMCID: PMC2659244
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M805937200
Structural determinants of integrin binding to the talin rod
Abstract
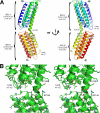
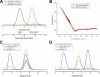
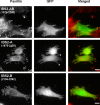
The adaptor protein talin serves both to activate the integrin family of cell adhesion molecules and to couple integrins to the actin cytoskeleton. Integrin activation has been shown to involve binding of the talin FERM domain to membrane proximal sequences in the cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta-subunit. However, a second integrin-binding site (IBS2) has been identified near the C-terminal end of the talin rod. Here we report the crystal structure of IBS2 (residues 1974-2293), which comprises two five-helix bundles, "IBS2-A" (1974-2139) and "IBS2-B" (2140-2293), connected by a continuous helix with a distinct kink at its center that is stabilized by side-chain H-bonding. Solution studies using small angle x-ray scattering and NMR point to a fairly flexible quaternary organization. Using pull-down and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, we demonstrate that integrin binding requires both IBS2 domains, as does binding to acidic phospholipids and robust targeting to focal adhesions. We have defined the membrane proximal region of the integrin cytoplasmic domain as the major binding region, although more membrane distal regions are also required for strong binding. Alanine-scanning mutagenesis points to an important electrostatic component to binding. Thermal unfolding experiments show that integrin binding induces conformational changes in the IBS2 module, which we speculate are linked to vinculin and membrane binding.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of vinculin in complex with vinculin binding site 50 (VBS50), the integrin binding site 2 (IBS2) of talin.Protein Sci. 2012 Apr;21(4):583-8. doi: 10.1002/pro.2041. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Protein Sci. 2012. PMID: 22334306 Free PMC article.
-
The talin rod IBS2 alpha-helix interacts with the beta3 integrin cytoplasmic tail membrane-proximal helix by establishing charge complementary salt bridges.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 29;283(35):24212-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709704200. Epub 2008 Jun 23. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18577523 Free PMC article.
-
The integrin binding site 2 (IBS2) in the talin rod domain is essential for linking integrin beta subunits to the cytoskeleton.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jun 8;282(23):17280-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611846200. Epub 2007 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17430904
-
Integrin connections to the cytoskeleton through talin and vinculin.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Apr;36(Pt 2):235-9. doi: 10.1042/BST0360235. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18363566 Review.
-
Integrin-mediated cell adhesion: the cytoskeletal connection.Biochem Soc Symp. 1999;65:79-99. Biochem Soc Symp. 1999. PMID: 10320934 Review.
Cited by
-
The dual structural roles of the membrane distal region of the α-integrin cytoplasmic tail during integrin inside-out activation.J Cell Sci. 2015 May 1;128(9):1718-31. doi: 10.1242/jcs.160663. Epub 2015 Mar 6. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 25749862 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient alpha helix model and simulation framework for stationary electrostatic interaction force estimation.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 27;11(1):9053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88369-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33907198 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of talin-dependent integrin signaling and crosstalk.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1838(2):579-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.07.017. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23891718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammary gland ECM remodeling, stiffness, and mechanosignaling in normal development and tumor progression.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Jan 1;3(1):a003228. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003228. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 20980442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The extracellular matrix-myosin pathway in mechanotransduction: from molecule to tissue.Emerg Top Life Sci. 2018 Dec 21;2(5):727-737. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20180043. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 33530663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Critchley, D. R., and Gingras, A. R. (2008) J. Cell Sci. 121 1345-1347 - PubMed
-
- McLachlan, A. D., Stewart, M., Hynes, R. O., and Rees, D. J. (1994) J. Mol. Biol. 235 1278-1290 - PubMed
-
- Gingras, A. R., Ziegler, W. H., Frank, R., Barsukov, I. L., Roberts, G. C., Critchley, D. R., and Emsley, J. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280 37217-37224 - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Alvarez, B., de Pereda, J. M., Calderwood, D. A., Ulmer, T. S., Critchley, D., Campbell, I. D., Ginsberg, M. H., and Liddington, R. C. (2003) Mol. Cell 11 49-58 - PubMed
-
- Wegener, K. L., Partridge, A. W., Han, J., Pickford, A. R., Liddington, R. C., Ginsberg, M. H., and Campbell, I. D. (2007) Cell 128 171-182 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

