A facile method for expression and purification of the Alzheimer's disease-associated amyloid beta-peptide
- PMID: 19175671
- PMCID: PMC2702495
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06862.x
A facile method for expression and purification of the Alzheimer's disease-associated amyloid beta-peptide
Abstract
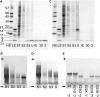
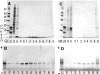
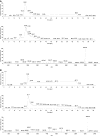
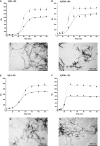
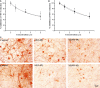
We report the development of a high-level bacterial expression system for the Alzheimer's disease-associated amyloid beta-peptide (Abeta), together with a scaleable and inexpensive purification procedure. Abeta(1-40) and Abeta(1-42) coding sequences together with added ATG codons were cloned directly into a Pet vector to facilitate production of Met-Abeta(1-40) and Met-Abeta(1-42), referred to as Abeta(M1-40) and Abeta(M1-42), respectively. The expression sequences were designed using codons preferred by Escherichia coli, and the two peptides were expressed in this host in inclusion bodies. Peptides were purified from inclusion bodies using a combination of anion-exchange chromatography and centrifugal filtration. The method described requires little specialized equipment and provides a facile and inexpensive procedure for production of large amounts of very pure Abeta peptides. Recombinant peptides generated using this protocol produced amyloid fibrils that were indistinguishable from those formed by chemically synthesized Abeta1-40 and Abeta1-42. Formation of fibrils by all peptides was concentration-dependent, and exhibited kinetics typical of a nucleation-dependent polymerization reaction. Recombinant and synthetic peptides exhibited a similar toxic effect on hippocampal neurons, with acute treatment causing inhibition of MTT reduction, and chronic treatment resulting in neuritic degeneration and cell loss.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression and purification of 15N- and 13C-isotope labeled 40-residue human Alzheimer's β-amyloid peptide for NMR-based structural analysis.Protein Expr Purif. 2011 Sep;79(1):16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2011.05.012. Epub 2011 May 27. Protein Expr Purif. 2011. PMID: 21640828 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and purification of amyloid-beta peptides from Escherichia coli.Protein Expr Purif. 2009 Jul;66(1):107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2009.02.009. Epub 2009 Feb 20. Protein Expr Purif. 2009. PMID: 19233290 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of peptides that specifically bind Abeta1-40 amyloid in vitro and amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease brain using phage display.Neurobiol Dis. 2003 Oct;14(1):146-56. doi: 10.1016/s0969-9961(03)00105-0. Neurobiol Dis. 2003. PMID: 13678675
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
-
Electrochemistry of Alzheimer Disease Amyloid Beta Peptides.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(33):4066-4083. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180214112536. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29446720 Review.
Cited by
-
Atomic Resolution Structure of Monomorphic Aβ42 Amyloid Fibrils.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Aug 3;138(30):9663-74. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b05129. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 27355699 Free PMC article.
-
Chirality Dependence of Amyloid β Cellular Uptake and a New Mechanistic Perspective.Chembiochem. 2019 Apr 15;20(8):1023-1026. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201800708. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Chembiochem. 2019. PMID: 30550626 Free PMC article.
-
An aggregation inhibitor specific to oligomeric intermediates of Aβ42 derived from phage display libraries of stable, small proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 May 24;119(21):e2121966119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2121966119. Epub 2022 May 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35580187 Free PMC article.
-
Designed peptides as nanomolar cross-amyloid inhibitors acting via supramolecular nanofiber co-assembly.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 25;13(1):5004. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32688-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36008417 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of N-Terminal Residues on the Assembly of Constrained β-Hairpin Peptides Derived from Aβ.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Jul 1;142(26):11593-11601. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c05186. Epub 2020 Jun 22. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32501687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins and therapies. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:742–761. - PubMed
-
- Tabaton M, Nunzi MG, Xue R, Usiak M, Autilio-Gambetti L, Gambetti P. Soluble amyloid β-protein is a marker of Alzheimer amyloid in brain but not in cerebrospinal fluid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;200:1598–1603. - PubMed
-
- Vigo-Pelfrey C, Lee D, Keim PS, Lieberburg I, Schenk D. Characterization of β-amyloid peptide from human cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem. 1993;61:1965–1968. - PubMed
-
- Naslund J, Karlstrom AR, Tjernberg LO, Schierhorn A, Terenius L, Nordstedt C. High-resolution separation of amyloid β-peptides: structural variants present in Alzheimer’s disease amyloid. J Neurochem. 1996;67:294–301. - PubMed
-
- Maler JM, Klafki HW, Paul S, Spitzer P, Groemer TW, Henkel AW, Esselmann H, Lewczuk P, Kornhuber J, Wiltfang J. Urea-based two-dimensional electrophoresis of β-amyloid peptides in human plasma: evidence for novel Abeta species. Proteomics. 2007;7:3815–3820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

