Human circulating CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ regulatory T cells kill autologous CD8+ but not CD4+ responder cells by Fas-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 19155494
- PMCID: PMC3721355
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.3.1469
Human circulating CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ regulatory T cells kill autologous CD8+ but not CD4+ responder cells by Fas-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
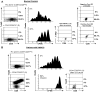
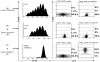
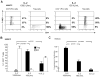
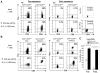
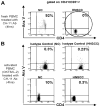
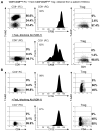
Mechanisms utilized by human regulatory T cells (Treg) for elimination of effector cells may vary. We investigated the possibility that the mechanism of Treg suppression depends on Fas/FasL-mediated apoptosis of responder cells (RC). CD4(+)CD25(high)Foxp3(+) Treg and autologous CD4(+)CD25(-) and CD8(+)CD25(-) subsets of RC were isolated from blood of 25 cancer patients and 15 normal controls and cocultured in the presence of OKT3 and IL-2 (150 or 1000 IU/ml). Suppression of RC proliferation was measured in CFSE assays. RC and Treg apoptosis was monitored by 7-aminoactinomycin D staining in flow-based cytotoxicity assays. Treg from all subjects expressed CD95(+), but only Treg from cancer patients expressed CD95L. These Treg, when activated via TCR plus IL-2, up-regulated CD95 and CD95L expression (p < 0.001) and suppressed CD8(+) RC proliferation (p < 0.001) by inducing Fas-mediated apoptosis. However, Treg cocultured with CD4(+) RC suppressed proliferation independently of Fas/FasL. In cocultures, Treg were found to be resistant to apoptosis in the presence of 1000 IU/ml IL-2, but at lower IL-2 concentrations (150 IU/ml) they became susceptible to RC-induced death. Thus, Treg and RC can reciprocally regulate Treg survival, depending on IL-2 concentrations present in cocultures. This divergent IL-2-dependent resistance or sensitivity of Treg and RC to apoptosis is amplified in patients with cancer.
Figures
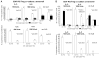
Similar articles
-
Reciprocal granzyme/perforin-mediated death of human regulatory and responder T cells is regulated by interleukin-2 (IL-2).J Mol Med (Berl). 2010 Jun;88(6):577-88. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0602-9. Epub 2010 Mar 12. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20225066 Free PMC article.
-
A unique subset of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T cells secreting interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta1 mediates suppression in the tumor microenvironment.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Aug 1;13(15 Pt 1):4345-54. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0472. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17671115
-
Expression of ICOS on human melanoma-infiltrating CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T regulatory cells: implications and impact on tumor-mediated immune suppression.J Immunol. 2008 Mar 1;180(5):2967-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.2967. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18292519
-
Functional and phenotypic characteristics of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ Treg clones obtained from peripheral blood of patients with cancer.Int J Cancer. 2007 Dec 1;121(11):2473-83. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23001. Int J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17691114
-
Akt-Fas to Quell Aberrant T Cell Differentiation and Apoptosis in Covid-19.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 21;11:600405. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.600405. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33408715 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reciprocal granzyme/perforin-mediated death of human regulatory and responder T cells is regulated by interleukin-2 (IL-2).J Mol Med (Berl). 2010 Jun;88(6):577-88. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0602-9. Epub 2010 Mar 12. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20225066 Free PMC article.
-
The Pivotal Role of Regulatory T Cells in the Regulation of Innate Immune Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 9;10:680. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00680. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31024539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Should a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) agonist or antagonist be designed to treat cancer? TLR-4: its expression and effects in the ten most common cancers.Onco Targets Ther. 2013 Nov 5;6:1573-87. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S50838. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 24235843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cell-tumor interaction directs the development of immunotherapies in head and neck cancer.Clin Dev Immunol. 2010;2010:236378. doi: 10.1155/2010/236378. Epub 2010 Dec 27. Clin Dev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21234340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD8⁺ Treg cells associated with decreasing disease activity after intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy in lupus nephritis with heavy proteinuria.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e81344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081344. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liyanage UK, Moore TT, Joo HG, Tanaka Y, Herrmann V, Doherty G, Drebin JA, Strasberg SM, Eberlein TJ, Goedegebuure PS, Linehan DC. Prevalence of regulatory T cells is increased in peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment of patients with pancreas or breast adenocarcinoma. J Immunol. 2002;169:2756–2761. - PubMed
-
- Strauss L, Bergmann C, Szczepanski MJ, Gooding W, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL. A unique subset of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T cells secreting IL-10 and TGF-β1 mediates suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4345–4354. - PubMed
-
- Hildeman DA, Zhu Y, Mitchell TC, Kappler J, Marrack P. Molecular mechanisms of activated T cell death in vivo. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:354–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

