Host ER-parasitophorous vacuole interaction provides a route of entry for antigen cross-presentation in Toxoplasma gondii-infected dendritic cells
- PMID: 19153244
- PMCID: PMC2646567
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20082108
Host ER-parasitophorous vacuole interaction provides a route of entry for antigen cross-presentation in Toxoplasma gondii-infected dendritic cells
Abstract
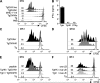
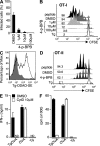
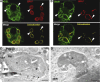
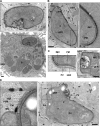
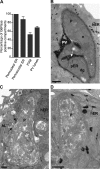
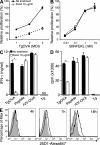
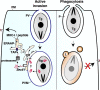
Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites infect host cells by an active invasion process leading to the formation of a specialized compartment, the parasitophorous vacuole (PV). PVs resist fusion with host cell endosomes and lysosomes and are thus distinct from phagosomes. Because the parasite remains sequestered within the PV, it is unclear how T. gondii-derived antigens (Ag's) access the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I pathway for presentation to CD8(+) T cells. We demonstrate that recruitment of host endoplasmic reticulum (hER) to the PV in T. gondii-infected dendritic cells (DCs) directly correlates with cross-priming of CD8(+) T cells. Furthermore, we document by immunoelectron microscopy the transfer of hER components into the PV, a process indicative of direct fusion between the two compartments. In strong contrast, no association between hER and phagosomes or Ag presentation activity was observed in DCs containing phagocytosed live or dead parasites. Importantly, cross-presentation of parasite-derived Ag in actively infected cells was blocked when hER retrotranslocation was inhibited, indicating that the hER serves as a conduit for the transport of Ag between the PV and host cytosol. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that pathogen-driven hER-PV interaction can serve as an important mechanism for Ag entry into the MHC class I pathway and CD8(+) T cell cross-priming.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rhoptry and Dense Granule Secreted Effectors Regulate CD8+ T Cell Recognition of Toxoplasma gondii Infected Host Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 6;10:2104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02104. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31555296 Free PMC article.
-
MHC I presentation of Toxoplasma gondii immunodominant antigen does not require Sec22b and is regulated by antigen orientation at the vacuole membrane.Eur J Immunol. 2017 Jul;47(7):1160-1170. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646859. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Eur J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28508576
-
Subcellular antigen location influences T-cell activation during acute infection with Toxoplasma gondii.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022936. Epub 2011 Jul 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829561 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii and MHC-restricted antigen presentation: on degradation, transport and modulation.Int J Parasitol. 2001 Oct;31(12):1355-69. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(01)00260-0. Int J Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11566303 Review.
-
Autophagy in immunity against Toxoplasma gondii.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;335:251-65. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-00302-8_12. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19802569 Review.
Cited by
-
Rhoptry and Dense Granule Secreted Effectors Regulate CD8+ T Cell Recognition of Toxoplasma gondii Infected Host Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 6;10:2104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02104. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31555296 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of Exogenous Antigens to Induce Cytotoxic CD8+ T Lymphocyte Responses.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:218752. doi: 10.1155/2010/218752. Epub 2010 May 23. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20508846 Free PMC article.
-
Parasite fate and involvement of infected cells in the induction of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses to Toxoplasma gondii.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Apr 10;10(4):e1004047. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004047. eCollection 2014 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24722202 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted Effectors Modulating Immune Responses to Toxoplasma gondii.Life (Basel). 2021 Sep 20;11(9):988. doi: 10.3390/life11090988. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34575137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on the identification and role of Toxoplasma gondii antigenic epitopes.Parasitol Res. 2016 Feb;115(2):459-68. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4824-1. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Parasitol Res. 2016. PMID: 26581372 Review.
References
-
- Mellman I., Steinman R.M. 2001. Dendritic cells: specialized and regulated antigen processing machines.Cell. 106:255–258 - PubMed
-
- Trombetta E.S., Mellman I. 2005. Cell biology of antigen processing in vitro and in vivo.Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23:975–1028 - PubMed
-
- Burgdorf S., Scholz C., Kautz A., Tampe R., Kurts C. 2008. Spatial and mechanistic separation of cross-presentation and endogenous antigen presentation.Nat. Immunol. 9:558–566 - PubMed
-
- Carruthers V.B., Sibley L.D. 1997. Sequential protein secretion from three distinct organelles of Toxoplasma gondii accompanies invasion of human fibroblasts.Eur. J. Cell Biol. 73:114–123 - PubMed
-
- Mordue D.G., Hakansson S., Niesman I., Sibley L.D. 1999. Toxoplasma gondii resides in a vacuole that avoids fusion with host cell endocytic and exocytic vesicular trafficking pathways.Exp. Parasitol. 92:87–99 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

