Nrf2 increases survival and attenuates alveolar growth inhibition in neonatal mice exposed to hyperoxia
- PMID: 19151108
- PMCID: PMC2670765
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90487.2008
Nrf2 increases survival and attenuates alveolar growth inhibition in neonatal mice exposed to hyperoxia
Abstract
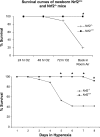
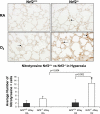
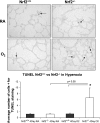
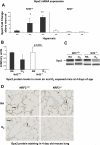
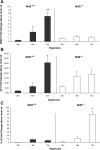
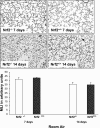
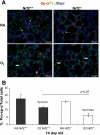
Increased oxidative stress is associated with perinatal asphyxia and respiratory distress in the newborn period. Induction of nuclear factor erythroid 2 p45-related factor (Nrf2) has been shown to decrease oxidative stress through the regulation of specific gene pathways. We hypothesized that Nrf2 attenuates mortality and alveolar growth inhibition in newborn mice exposed to hyperoxia. Nrf2(+/+) and Nrf2(-/-) newborn mice were exposed to hyperoxia at 24 h. Survival was significantly less in Nrf2(-/-) mice exposed to 72 h of hyperoxia and returned to room air (P < 0.0001) and in Nrf2(-/-) mice exposed to hyperoxia for 8 continuous days (P < 0.005). To determine the response of Nrf2 target genes to hyperoxia, glutathione peroxidase 2 (Gpx2) and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1) expression was measured from lung of newborn mice using real-time PCR. In the Nrf2(+/+) mice, significant induction of lung Gpx2 and NQO1 above room air controls was found with hyperoxia. In contrast, Nrf2(-/-) mice had minimal induction of lung Gpx2 and NQO1 with hyperoxia. Expression of p21 and IL-6, genes not regulated by Nrf2, were also measured. IL-6 expression in Nrf2(-/-) lung was markedly induced by 72 h of hyperoxia in contrast to the Nrf2(+/+) mice. p21 was induced in both Nrf2(+/+) and Nrf2(-/-) lung by hyperoxia. Mean linear intercept (MLI) and mean chord length (MCL) were significantly increased in 14-day-old Nrf2(-/-) mice previously exposed to hyperoxia compared with Nrf2(+/+) mice. The percentage of surfactant protein C (Sp-c(+)) type 2 alveolar cells in 14-day-old Nrf2(-/-) mice exposed to neonatal hyperoxia was also significantly less than Nrf2(+/+) mice (P < 0.02). In summary, these findings indicate that Nrf2 increases survival in newborn mice exposed to hyperoxia and that Nrf2 may help attenuate alveolar growth inhibition caused by hyperoxia exposure.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibition Attenuates Neonatal Hyperoxic Lung Injury and Enhances Nuclear Factor E2-Related Factor 2 Activation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Sep;55(3):419-28. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0228OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27089175 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional responses of neonatal mouse lung to hyperoxia by Nrf2 status.Cytokine. 2014 Jan;65(1):4-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Cytokine. 2014. PMID: 24139870 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperoxia impairs postnatal alveolar epithelial development via NADPH oxidase in newborn mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):L134-42. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00112.2009. Epub 2009 May 1. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19411313 Free PMC article.
-
The NRF2 activation and antioxidative response are not impaired overall during hyperoxia-induced lung epithelial cell death.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:798401. doi: 10.1155/2013/798401. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 23738042 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted deletion of nrf2 impairs lung development and oxidant injury in neonatal mice.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Oct 15;17(8):1066-82. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4288. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22400915 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Postnatal inflammation in the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2014 Mar;100(3):189-201. doi: 10.1002/bdra.23220. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2014. PMID: 24578018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postnatal Hyperoxia Exposure Durably Impairs Right Ventricular Function and Mitochondrial Biogenesis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017 May;56(5):609-619. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0256OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28129517 Free PMC article.
-
NRF2 and cancer: the good, the bad and the importance of context.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Jul 19;12(8):564-71. doi: 10.1038/nrc3278. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22810811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR): A Novel Therapeutic Target for Pulmonary Diseases?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 28;23(3):1516. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031516. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heme oxygenase in neonatal lung injury and repair.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Nov 1;21(13):1881-92. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5791. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24382006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Audi SH, Bongard RD, Krenz GS, Rickaby DA, Haworth ST, Eisenhauer J, Roerig DL, Merker MP. Effect of chronic hyperoxic exposure on duroquinone reduction in adult rat lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289: L788–L797, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramaniam V, Mervis CF, Maxey AM, Markham NE, Abman SH. Hyperoxia reduces bone marrow, circulating, and lung endothelial progenitor cells in the developing lung: implications for the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292: L1073–L1084, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Baydas G, Karatas F, Gursu MF, Bozkurt HA, Ilhan N, Yasar A, Canatan H. Antioxidant vitamin levels in term and preterm infants and their relation to maternal vitamin status. Arch Med Res 33: 276–280, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Blanco LN, Frank L. The formation of alveoli in rat lung during the third and fourth postnatal weeks: effect of hyperoxia, dexamethasone, and deferoxamine. Pediatr Res 34: 334–340, 1993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

