The chemokine receptor CXCR4 and the metalloproteinase MT1-MMP are mutually required during melanoma metastasis to lungs
- PMID: 19147814
- PMCID: PMC2630568
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080636
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 and the metalloproteinase MT1-MMP are mutually required during melanoma metastasis to lungs
Abstract
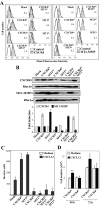
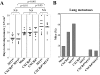
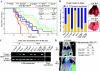
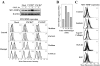
Melanoma is the most aggressive skin cancer once metastasis begins; therefore, it is important to characterize the molecular players involved in melanoma dissemination. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 and the membrane-bound metalloproteinase MT1-MMP are expressed on melanoma cells and represent candidate molecules for the control of metastasis. Using human melanoma transfectants that either overexpress or silence CXCR4 or MT1-MMP, or that have a combination of overexpression and interference of these proteins, we show that CXCR4 and MT1-MMP coordinate their activities at different steps along melanoma cell metastasis into the lungs. Results from in vivo xenograft mouse models of melanoma lung colonization and mice survival and short-term, homing nested polymerase chain reaction experiments from lung samples indicated that CXCR4 is required at early phases of melanoma cell arrival in the lungs. In contrast, MT1-MMP is not needed for these initial steps but promotes subsequent invasion and dissemination of the tumor with CXCR4. Investigation of potential cross talk between CXCR4 and MT1-MMP revealed that MT1-MMP accumulates intracellularly after melanoma cell stimulation with the CXCR4 ligand CXCL12, and that this process involves the activation of the Rac-Erk1/2 pathway. Subsequent to cell contact with specific basement membrane proteins, MT1-MMP redistributes to the cell membrane in a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent manner. These results suggest that combination therapies that target CXCR4 and MT1-MMP should improve the limitations of the current therapies for metastatic melanoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MT1-MMP modulates melanoma cell dissemination and metastasis through activation of MMP2 and RAC1.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014 Mar;27(2):287-96. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12201. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014. PMID: 24387669
-
The tetraspanin CD81 protein increases melanoma cell motility by up-regulating metalloproteinase MT1-MMP expression through the pro-oncogenic Akt-dependent Sp1 activation signaling pathways.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15691-704. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.534206. Epub 2014 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24733393 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and its co-localization with membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) correlate with melanoma progression.J Pathol. 2000 Jul;191(3):245-56. doi: 10.1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH632>3.0.CO;2-#. J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10878545
-
The membrane tethered matrix metalloproteinase MT1-MMP at the forefront of melanoma cell invasion and metastasis.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Sep;111:17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.05.019. Epub 2016 May 21. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27221755 Review.
-
Is it possible to treat melanoma by intercepting the CXCR4/CXCL12 pathway?Cytokine. 2024 Jul;179:156629. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156629. Epub 2024 May 4. Cytokine. 2024. PMID: 38704961 Review.
Cited by
-
Interplay of adherens junctions and matrix proteolysis determines the invasive pattern and growth of squamous cell carcinoma.Elife. 2023 Mar 9;12:e76520. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76520. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36892272 Free PMC article.
-
New Strategies for the Next Generation of Matrix-Metalloproteinase Inhibitors: Selectively Targeting Membrane-Anchored MMPs with Therapeutic Antibodies.Biochem Res Int. 2011;2011:191670. doi: 10.1155/2011/191670. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Biochem Res Int. 2011. PMID: 21152183 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocytes as paracrine regulators of metastasis and determinants of organ-specific colonization.Int J Cancer. 2011 Jun 1;128(11):2536-44. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26032. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21387299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of nimotuzumab in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Biologics. 2010 Nov 9;4:289-98. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S8617. Biologics. 2010. PMID: 21116327 Free PMC article.
-
TIMP-1 induces an EMT-like phenotypic conversion in MDCK cells independent of its MMP-inhibitory domain.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038773. Epub 2012 Jun 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22701711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:563–572. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:540–550. - PubMed
-
- Müller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, Barrera JL, Mohar A, Verastegui E, Zlotnik A. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2001;410:50–56. - PubMed
-
- Robledo MM, Bartolome RA, Longo N, Rodriguez-Frade JM, Mellado M, Longo I, van Muijen GN, Sanchez-Mateos P, Teixido J. Expression of functional chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CXCR4 on human melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:45098–45105. - PubMed
-
- Murakami T, Maki W, Cardones AR, Fang H, Tun Kyi A, Nestle FO, Hwang ST. Expression of CXC chemokine receptor-4 enhances the pulmonary metastatic potential of murine B16 melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7328–7334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

