SUG-1 plays proteolytic and non-proteolytic roles in the control of retinoic acid target genes via its interaction with SRC-3
- PMID: 19144644
- PMCID: PMC2658106
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808815200
SUG-1 plays proteolytic and non-proteolytic roles in the control of retinoic acid target genes via its interaction with SRC-3
Abstract
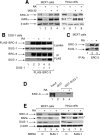
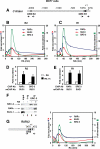
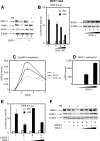
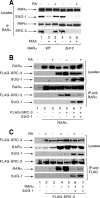
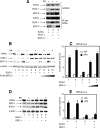
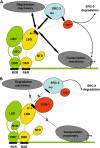
Nuclear retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARalpha) activates gene expression through dynamic interactions with coregulatory protein complexes, the assembly of which is directed by the ligand and the AF-2 domain of RARalpha. Then RARalpha and its coactivator SRC-3 are degraded by the proteasome. Recently it has emerged that the proteasome also plays a key role in RARalpha-mediated transcription. Here we show that SUG-1, one of the six ATPases of the 19 S regulatory complex of the 26 S proteasome, interacts with SRC-3, is recruited at the promoters of retinoic acid (RA) target genes, and thereby participates to their transcription. In addition, SUG-1 also mediates the proteasomal degradation of SRC-3. However, when present in excess amounts, SUG-1 blocks the activation of RARalpha target genes and the degradation of RARalpha that occurs in response to RA, via its ability to interfere with the recruitment of SRC-3 and other coregulators at the AF-2 domain of RARalpha. We propose a model in which the ratio between SUG-1 and SRC-3 is crucial for the control of RARalpha functioning. This study provides new insights into how SUG-1 has a unique role in linking the transcription and degradation processes via its ability to interact with SRC-3.
Figures

Similar articles
-
P38MAPK-dependent phosphorylation and degradation of SRC-3/AIB1 and RARalpha-mediated transcription.EMBO J. 2006 Feb 22;25(4):739-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600981. Epub 2006 Feb 2. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16456540 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of STAT5b-RARalpha, a novel acute promyelocytic leukemia fusion protein, with retinoic acid receptor and STAT3 signaling pathways.Blood. 2002 Apr 15;99(8):2637-46. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.8.2637. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11929748
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent regulation of SRC-3 and involvement in retinoic acid receptor alpha signaling in embryonic cortical neurons.IUBMB Life. 2009 Jun;61(6):670-8. doi: 10.1002/iub.212. IUBMB Life. 2009. PMID: 19472184
-
Protein kinases and the proteasome join in the combinatorial control of transcription by nuclear retinoic acid receptors.Trends Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;17(6):302-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.04.003. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Trends Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17467991 Review.
-
Dynamic and combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs).Nucl Recept Signal. 2009 May 8;7:e005. doi: 10.1621/nrs.07005. Nucl Recept Signal. 2009. PMID: 19471584 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of RPT6 Controls Its Ability to Bind DNA and Regulate Gene Expression in the Hippocampus of Male Rats during Memory Formation.J Neurosci. 2024 Jan 24;44(4):e1453232023. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1453-23.2023. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38124005 Free PMC article.
-
Cullin 3 mediates SRC-3 ubiquitination and degradation to control the retinoic acid response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 20;108(51):20603-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102572108. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22147914 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Feedback Regulation of Vitamin A Metabolism.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 21;14(6):1312. doi: 10.3390/nu14061312. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35334970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasomal interaction as a critical activity modulator of the human constitutive androstane receptor.Biochem J. 2014 Feb 15;458(1):95-107. doi: 10.1042/BJ20130685. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 24224465 Free PMC article.
-
Trifarotene: A Current Review and Perspectives in Dermatology.Biomedicines. 2021 Feb 26;9(3):237. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9030237. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33652835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Germain, P., Staels, B., Dacquet, C., Spedding, M., and Laudet, V. (2006) Pharmacol. Rev. 58 685-704 - PubMed
-
- Laudet, V., and Gronemeyer, H. (2001) Nuclear Receptor Factsbook, Academic Press, London
-
- Chambon, P. (1996) FASEB J. 10 940-954 - PubMed
-
- Glass, C. K., and Rosenfeld, M. G. (2000) Genes Dev. 14 121-141 - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre, P., Martin, P. J., Flajollet, S., Dedieu, S., Billaut, X., and Lefebvre, B. (2005) Vitam. Horm. 70 199-264 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

