Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein
- PMID: 19144316
- PMCID: PMC2654249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.010
Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein
Abstract
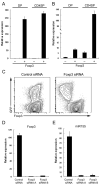
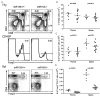
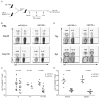
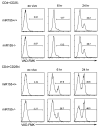
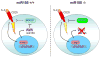
Foxp3(+) regulatory T (Treg) cells limit pathogenic immune responses to self-antigens and foreign antigens. An essential role for microRNA (miRNA) in the maintenance and function of Treg cells, revealed by the Treg cell-specific Dicer ablation, raised a question as to a specific miRNA contribution. We found that Foxp3 controlled the elevated miR155 expression required for maintaining Treg cell proliferative activity and numbers under nonlymphopenic conditions. Moreover, miR155 deficiency in Treg cells resulted in increased suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) expression accompanied by impaired activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) transcription factor in response to limiting amounts of interleukin-2. Our studies suggest that Foxp3-dependent regulation of miR155 maintains competitive fitness of Treg cell subsets by targeting SOCS1, and they provide experimental support for a proposed role for miRNAs in ensuring the robustness of cellular phenotypes.
Figures

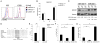
Similar articles
-
Enhancement of Immunoregulatory Function of Modified Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Targeting SOCS1.Biomed Res Int. 2018 May 8;2018:3530647. doi: 10.1155/2018/3530647. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29854745 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SOCS1-/- lethal autoinflammatory disease correlated to enhanced peripheral Foxp3+ regulatory T cell homeostasis.J Immunol. 2011 Sep 1;187(5):2666-76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003819. Epub 2011 Jul 25. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21788442 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS1 is essential for regulatory T cell functions by preventing loss of Foxp3 expression as well as IFN-{gamma} and IL-17A production.J Exp Med. 2011 Sep 26;208(10):2055-67. doi: 10.1084/jem.20110428. Epub 2011 Sep 5. J Exp Med. 2011. PMID: 21893603 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS1 and regulation of regulatory T cells plasticity.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:943149. doi: 10.1155/2014/943149. Epub 2014 Jul 15. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 25133199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
SOCS1 is significantly up-regulated in Nutlin-3-treated p53wild-type B chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) samples and shows an inverse correlation with miR-155.Invest New Drugs. 2012 Dec;30(6):2403-6. doi: 10.1007/s10637-011-9786-2. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22238073
-
MicroRNA regulation of lymphocyte tolerance and autoimmunity.J Clin Invest. 2015 Jun;125(6):2242-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI78090. Epub 2015 Jun 1. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26030228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A miR-155-Peli1-c-Rel pathway controls the generation and function of T follicular helper cells.J Exp Med. 2016 Aug 22;213(9):1901-19. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160204. Epub 2016 Aug 1. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27481129 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of acute graft-versus-host disease by microRNA-155.Blood. 2012 May 17;119(20):4786-97. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-387522. Epub 2012 Mar 9. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22408260 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids suppress T cell function by up-regulating microRNA-98.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Jul;65(7):1882-90. doi: 10.1002/art.37966. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23575983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bayer AL, Yu A, Malek TR. Function of the IL-2R for thymic and peripheral CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J Immunol. 2007;178:4062–4071. - PubMed
-
- Cornish AL, Chong MM, Davey GM, Darwiche R, Nicola NA, Hilton DJ, Kay TW, Starr R, Alexander WS. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 regulates signaling in response to interleukin-2 and other gamma c-dependent cytokines in peripheral T cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:22755–22761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

