Dynamic regulation of Pdx1 enhancers by Foxa1 and Foxa2 is essential for pancreas development
- PMID: 19141476
- PMCID: PMC2607077
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1752608
Dynamic regulation of Pdx1 enhancers by Foxa1 and Foxa2 is essential for pancreas development
Abstract
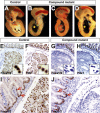
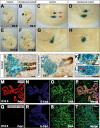
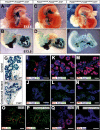
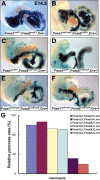
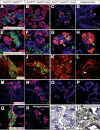
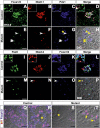
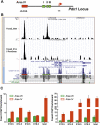
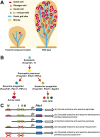
The onset of pancreas development in the foregut endoderm is marked by activation of the homeobox gene Pdx1 (IPF1). Pdx1 is essential for the expansion of the pancreatic primordium and the development of endocrine islets. The control of Pdx1 expression has been only partially elucidated. We demonstrate here that the winged-helix transcription factors Foxa1 and Foxa2 co-occupy multiple regulatory domains in the Pdx1 gene. Compound conditional ablation of both Foxa1 and Foxa2 in the pancreatic primordium results in complete loss of Pdx1 expression and severe pancreatic hypoplasia. Mutant mice exhibit hyperglycemia with severely disrupted acinar and islet development, and die shortly after birth. Assessment of developmental markers in the mutant pancreas revealed a failure in the expansion of the pancreatic anlage, a blockage of exocrine and endocrine cell differentiation, and an arrest at the primitive duct stage. Comparing their relative developmental activity, we find that Foxa2 is the major regulator in promoting pancreas development and cell differentiation. Using chromatin immunoprecipitations (ChIP) and ChIP sequencing (ChIPSeq) of fetal pancreas and islet chromatin, we demonstrate that Foxa1 and Foxa2 predominantly occupy a distal enhancer at -6.4 kb relative to the transcriptional start site in the Pdx1 gene. In addition, occupancy of the well-characterized proximal Pdx1 enhancer by Foxa1 and Foxa2 is developmental stage-dependent. Thus, the regulation of Pdx1 expression by Foxa1 and Foxa2 is a key early event controlling the expansion and differentiation of the pancreatic primordia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Foxa2 and Pdx1 cooperatively regulate postnatal maturation of pancreatic β-cells.Mol Metab. 2017 Mar 25;6(6):524-534. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.03.007. eCollection 2017 Jun. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28580283 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional Tissue-Specific Foxa2 Ablation in Mouse Pancreas Causes Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia.Am J Ther. 2016 Nov/Dec;23(6):e1442-e1448. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000399. Am J Ther. 2016. PMID: 26882312
-
Foxa2 controls Pdx1 gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells in vivo.Diabetes. 2002 Aug;51(8):2546-51. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.8.2546. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 12145169
-
Winged-helix transcription factors and pancreatic development.Clin Sci (Lond). 2005 Mar;108(3):195-204. doi: 10.1042/CS20040309. Clin Sci (Lond). 2005. PMID: 15631623 Review.
-
Foxa1 and Foxa2 transcription factors regulate differentiation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;651:58-65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-0322-8_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19731550 Review.
Cited by
-
FOXA1 mediates p16(INK4a) activation during cellular senescence.EMBO J. 2013 Mar 20;32(6):858-73. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.35. Epub 2013 Feb 26. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23443045 Free PMC article.
-
Foxa1 and Foxa2 orchestrate development of the urethral tube and division of the embryonic cloaca through an autoregulatory loop with Shh.Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 1;465(1):23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.06.009. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32645357 Free PMC article.
-
The endocrine pancreas: insights into development, differentiation, and diabetes.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012 Sep-Oct;1(5):609-28. doi: 10.1002/wdev.44. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 23799564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRKAG2.2 is essential for FoxA1+ regulatory T cell differentiation and metabolic rewiring distinct from FoxP3+ regulatory T cells.Sci Adv. 2023 Dec 22;9(51):eadj8442. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj8442. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38117896 Free PMC article.
-
Examining How the MAFB Transcription Factor Affects Islet β-Cell Function Postnatally.Diabetes. 2019 Feb;68(2):337-348. doi: 10.2337/db18-0903. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 30425060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlgren U., Pfaff S.L., Jessell T.M., Edlund T., Edlund H. Independent requirement for ISL1 in formation of pancreatic mesenchyme and islet cells. Nature. 1997;385:257–260. - PubMed
-
- Apelqvist A., Li H., Sommer L., Beatus P., Anderson D.J., Honjo T., de Hrabe Angelis M., Lendahl U., Edlund H. Notch signalling controls pancreatic cell differentiation. Nature. 1999;400:877–881. - PubMed
-
- Behr R., Brestelli J., Fulmer J.T., Miyawaki N., Kleyman T.R., Kaestner K.H. Mild nephrogenic diabetes insipidus caused by Foxa1 deficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:41936–41941. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shushan E., Marshak S., Shoshkes M., Cerasi E., Melloul D. A pancreatic β-cell-specific enhancer in the human PDX-1 gene is regulated by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3β (HNF-3β), HNF-1α, and SPs transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:17533–17540. - PubMed
-
- Boyer D.F., Fujitani Y., Gannon M., Powers A.C., Stein R.W., Wright C.V. Complementation rescue of Pdx1 null phenotype demonstrates distinct roles of proximal and distal cis-regulatory sequences in pancreatic and duodenal expression. Dev. Biol. 2006;298:616–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
