Perioperative immune responses in cancer patients undergoing digestive surgeries
- PMID: 19138398
- PMCID: PMC2632631
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-7-7
Perioperative immune responses in cancer patients undergoing digestive surgeries
Abstract
Background: Th1/Th2 cell balance is thought to be shifted toward a Th2-type immune response not only by malignancy but also by surgical stress. The aim of this study was to estimate perioperative immune responses with respect to the Th1/Th2 balance in patients with gastrointestinal cancer.
Methods: Ninety-four patients who underwent abdominal surgeries were divided into three groups: gastric resection (n = 40), colorectal resection (n = 34) and hepatic resection (n = 20). Twelve patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy and 20 healthy subjects were served as control groups. Intracellular cytokine staining in CD4+ T lymphocytes was identified to characterize Th1/Th2 balance. Th1/Th2 balance was evaluated before operation and until postoperative days (POD) 14.
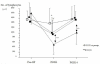
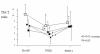
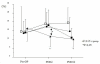
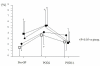
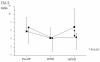
Results: The preoperative Th1/Th2 ratio was significantly lower in patients with malignancy compared with control. The Th1/Th2 ratio of patients in all groups decreased significantly postoperatively. Th1/Th2 balance on POD 2 in patients with malignancy was significantly decreased compared to patients with laparoscopic cholecystectomy, but there were no significant differences among the four groups on POD 14.
Conclusion: Patients with malignancy showed an abnormal perioperative Th1/Th2 balance suggesting predominance of a type-2 immune response. Major abdominal surgeries induce a marked shift in Th1/Th2 balance toward Th2 in the early postoperative stage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatic resection induces a shift in the Th 1/2 balance toward Th 2 and produces hypermetabolic and hyperhemodynamic states.Hepatogastroenterology. 2004 Sep-Oct;51(59):1422-7. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 15362768
-
Preoperative oral immune-enhancing nutritional supplementation corrects TH1/TH2 imbalance in patients undergoing elective surgery for colorectal cancer.Dis Colon Rectum. 2006 Apr;49(4):507-16. doi: 10.1007/s10350-005-0292-5. Dis Colon Rectum. 2006. PMID: 16421661 Clinical Trial.
-
Hepatic resection leads to predominance of the T helper-2 lymphocyte phenotype.Hepatol Res. 2004 Oct;30(2):96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.hepres.2004.07.003. Hepatol Res. 2004. PMID: 15519274
-
Does impaired TH1/TH2 balance cause postoperative infectious complications in colorectal cancer surgery?J Surg Res. 2007 May 1;139(1):15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2006.10.029. Epub 2007 Feb 9. J Surg Res. 2007. PMID: 17292403
-
Surgical stress induces a shift in the type-1/type-2 T-helper cell balance, suggesting down-regulation of cell-mediated and up-regulation of antibody-mediated immunity commensurate to the trauma.Surgery. 1996 Mar;119(3):316-25. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(96)80118-8. Surgery. 1996. PMID: 8619187
Cited by
-
Preoperative lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio predicts postoperative infectious complications after laparoscopic colorectal cancer surgery.Int J Clin Oncol. 2020 Apr;25(4):633-640. doi: 10.1007/s10147-019-01583-y. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Int J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31781993
-
Immune reaction by cytoreductive prostatectomy.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2019 Apr 25;7(2):64-79. eCollection 2019. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2019. PMID: 31139701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of immune responses of gastric cancer patients treated by laparoscopic and open gastrectomy.Med Oncol. 2015 Nov;32(11):253. doi: 10.1007/s12032-015-0699-3. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26471180
-
Malignancy is a risk factor for postoperative infectious complications after elective colorectal resection.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2016 Apr;31(4):885-94. doi: 10.1007/s00384-016-2521-x. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2016. PMID: 26838016
-
Inflammatory response and oxidative stress during liver resection.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 18;12(10):e0185685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185685. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29045432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sato M, Goto S, Kaneko R, Ito M, Sato S, Takeuchi S. Impaired production of Th1 cytokines and increased frequency of Th2 subsets in PBMC from advanced cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 1998;18:3951–3955. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. J Immunol. 1986;36:2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrini P, Berghella AM, Del Beato T, Cicia S, Adorno D, Casciani CU. Distribution in Th1 and Th2 subsets of CD4+T cells in peripheral blood of colorectal cancer patients and involvement in cancer establishment and progression. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1996;42:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s002620050244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elsasser-Beile U, Kolble N, Grussenmeyer T, Schultze-Seemann W, Wetterauer U, Gallati H, Schulte Mönting J, von Kleist S. Th1 and Th2 cytokine response patterns in leukocyte cultures of patients with urinary bladder, renal cell and prostate carcinomas. Tumor Biol. 1998;9:470–476. doi: 10.1159/000030039. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

