Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer
- PMID: 19125156
- PMCID: PMC2628455
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.137
Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer
Abstract
The pervasive influence of secreted Wnt signaling proteins in tissue homeostasis and tumorigenesis has galvanized efforts to identify small molecules that target Wnt-mediated cellular responses. By screening a diverse synthetic chemical library, we have discovered two new classes of small molecules that disrupt Wnt pathway responses; whereas one class inhibits the activity of Porcupine, a membrane-bound acyltransferase that is essential to the production of Wnt proteins, the other abrogates destruction of Axin proteins, which are suppressors of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activity. With these small molecules, we establish a chemical genetic approach for studying Wnt pathway responses and stem cell function in adult tissue. We achieve transient, reversible suppression of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway response in vivo, and we establish a mechanism-based approach to target cancerous cell growth. The signal transduction mechanisms shown here to be chemically tractable additionally contribute to Wnt-independent signal transduction pathways and thus could be broadly exploited for chemical genetics and therapeutic goals.
Figures
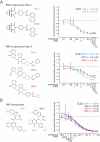
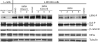





Comment in
-
Novel Wnt antagonists target porcupine and Axin.Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Feb;5(2):74-5. doi: 10.1038/nchembio0209-74. Nat Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19148172 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
[Dual-role regulations of canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010 Apr 18;42(2):238-42. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010. PMID: 20396373 Review. Chinese.
-
LRP6 transduces a canonical Wnt signal independently of Axin degradation by inhibiting GSK3's phosphorylation of beta-catenin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 10;105(23):8032-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803025105. Epub 2008 May 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18509060 Free PMC article.
-
Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling.Nature. 2009 Oct 1;461(7264):614-20. doi: 10.1038/nature08356. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19759537
-
Reconstituting regulation of the canonical Wnt pathway by engineering a minimal β-catenin destruction machine.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Jan 1;28(1):41-53. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-07-0557. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 27852897 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by protein kinases.Dev Dyn. 2010 Jan;239(1):34-44. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22019. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 19623618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin inhibits cardiac mesoderm, not mesendoderm, formation during cardiac differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells and modulation of canonical Wnt signaling can rescue this inhibition.Stem Cells. 2013 Mar;31(3):447-57. doi: 10.1002/stem.1289. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23193013 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin pathway in tissue injury: roles in pathology and therapeutic opportunities for regeneration.FASEB J. 2016 Oct;30(10):3271-3284. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600502R. Epub 2016 Jun 22. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 27335371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lef1 regulates Dusp6 to influence neuromast formation and spacing in the zebrafish posterior lateral line primordium.Development. 2013 Jun;140(11):2387-97. doi: 10.1242/dev.091348. Epub 2013 May 1. Development. 2013. PMID: 23637337 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivating mutations of RNF43 confer Wnt dependency in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 30;110(31):12649-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307218110. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23847203 Free PMC article.
-
A novel TNKS/USP25 inhibitor blocks the Wnt pathway to overcome multi-drug resistance in TNKS-overexpressing colorectal cancer.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Jan;14(1):207-222. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.10.013. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38261825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–80. - PubMed
-
- Van der Flier LG, et al. The Intestinal Wnt/TCF Signature. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:628–32. - PubMed
-
- Korinek V, et al. Depletion of epithelial stem-cell compartments in the small intestine of mice lacking Tcf-4. Nat Genet. 1998;19:379–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- PubChem-Substance/56413306
- PubChem-Substance/56413307
- PubChem-Substance/56413308
- PubChem-Substance/56413309
- PubChem-Substance/56413310
- PubChem-Substance/56413311
- PubChem-Substance/56413312
- PubChem-Substance/56413313
- PubChem-Substance/56413314
- PubChem-Substance/56413315
- PubChem-Substance/56413316
- PubChem-Substance/56413317
- PubChem-Substance/56413318
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases

