Endocannabinoid-dependent plasticity at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses in the striatum is regulated by synaptic activity
- PMID: 19120438
- PMCID: PMC2661034
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06551.x
Endocannabinoid-dependent plasticity at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses in the striatum is regulated by synaptic activity
Abstract
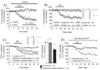
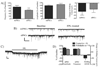
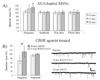
Long-term depression (LTD) at striatal synapses is mediated by postsynaptic endocannabinoid (eCB) release and presynaptic cannabinoid 1 receptor (CB(1)R) activation. Previous studies have indicated that eCB mobilization at excitatory synapses might be regulated by afferent activation. To further address the role of neuronal activity in synaptic plasticity we examined changes in synaptic strength induced by the L-type calcium channel activator 2,5-dimethyl-4-[2-(phenylmethyl)benzoyl]-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester (FPL 64176, FPL) at glutamatergic and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic synapses in the striatum. We found that the basic mechanisms for FPL-mediated eCB signaling are the same at glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses. FPL-induced LTD (FPL-LTD) was blocked in slices treated with the CB(1)R antagonist AM251 (2 microm), but established depression was not reversed by AM251. FPL-LTD was temperature dependent, blocked by protein translation inhibitors and prevented by intracellular loading of the anandamide transporter inhibitor VDM11 (10 microm) at both glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses. FPL-LTD at glutamatergic synapses required paired-pulse afferent stimulation, while FPL-LTD at GABAergic synapses could be induced even in the absence of explicit afferent activation. By evaluating tetrodotoxin-insensitive spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents we found that neuronal firing is vital for eCB release and LTD induction at GABAergic synapses, but not for short-term depression induced by CB(1)R agonist. The data presented here suggest that the level of neuronal firing regulates eCB signaling by modulating release from the postsynaptic cell, as well as interacting with presynaptic mechanisms to induce LTD at both glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses in the striatum.
Figures
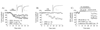
Comment in
-
Balancing excitation, inhibition and endocannabinoids (Commentary on Ademark et al.).Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Jan;29(1):31. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06603.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19120437 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling at striatal synapses requires a regulated postsynaptic release step.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 18;104(51):20564-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706873104. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18077376 Free PMC article.
-
A novel non-CB1/TRPV1 endocannabinoid-mediated mechanism depresses excitatory synapses on hippocampal CA1 interneurons.Hippocampus. 2012 Feb;22(2):209-21. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20884. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Hippocampus. 2012. PMID: 21069781 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of endocannabinoid release and striatal long-term depression by postsynaptic blockade of endocannabinoid membrane transport.J Neurosci. 2004 Feb 18;24(7):1673-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5214-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14973237 Free PMC article.
-
Wiring and firing neuronal networks: endocannabinoids take center stage.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008 Jun;18(3):338-45. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.08.007. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18801434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of endocannabinoid control of synaptic plasticity.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Oct 1;197:108736. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108736. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34343612 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism for differential recruitment of orbitostriatal transmission during actions and outcomes following chronic alcohol exposure.Elife. 2021 Mar 17;10:e67065. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67065. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33729155 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency-dependent inversion of net striatal output by endocannabinoid-dependent plasticity at different synaptic inputs.J Neurosci. 2009 Feb 4;29(5):1375-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3842-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19193884 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic long-term depression mediated by Gi/o-coupled receptors.Trends Neurosci. 2014 Nov;37(11):663-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2014.07.010. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Trends Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25160683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional status-dependent endocannabinoid signalling regulates the integration of rat visceral information.J Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;595(11):3267-3285. doi: 10.1113/JP273484. Epub 2017 Mar 27. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28233325 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation of nociceptive versus non-nociceptive synapses by endocannabinoids.Mol Pain. 2013 Jun 1;9:26. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-9-26. Mol Pain. 2013. PMID: 23725095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carter AG, Sabatini BL. State-dependent calcium signaling in dendritic spines of striatal medium spiny neurons. Neuron. 2004;44:483–493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

