Integrins and cell-fate determination
- PMID: 19118209
- PMCID: PMC2714415
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.018945
Integrins and cell-fate determination
Abstract
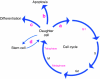
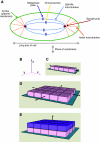
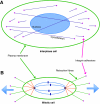
All cellular processes are determined by adhesive interactions between cells and their local microenvironment. Integrins, which constitute one class of cell-adhesion receptor, are multifunctional proteins that link cells to the extracellular matrix and organise integrin adhesion complexes at the cell periphery. Integrin-based adhesions provide anchor points for assembling and organising the cytoskeleton and cell shape, and for orchestrating migration. Integrins also control the fate and function of cells by influencing their proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. Moreover, new literature demonstrates that integrins control the cell-division axis at mitosis. This extends the influence of integrins over cell-fate decisions, as daughter cells are frequently located in new microenvironments that determine their behaviour following cell division. In this Commentary, I describe how integrins influence cell-fate determination, placing particular emphasis on their role in influencing the direction of cell division and the orientation of the mitotic spindle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Mitotic Cell-Substrate Adhesion Re-modeling in Animal Cell Division.Dev Cell. 2018 Apr 9;45(1):132-145.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.03.009. Dev Cell. 2018. PMID: 29634933
-
Cell shape and intercellular adhesion regulate mitotic spindle orientation.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Sep 1;30(19):2458-2468. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-04-0227. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31411941 Free PMC article.
-
Spindle orientation and epidermal morphogenesis.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Sep 23;368(1629):20130016. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0016. Print 2013. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24062586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic cell responses to substrate topological cues are independent of the molecular nature of adhesion.Sci Signal. 2020 Feb 25;13(620):eaax9940. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aax9940. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 32098802
-
Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: the dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor.J Endocrinol. 2011 May;209(2):139-51. doi: 10.1530/JOE-10-0377. Epub 2011 Feb 9. J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21307119 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific β-containing integrins exert differential control on proliferation and two-dimensional collective cell migration in mammary epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 13;287(29):24103-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.360834. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22511753 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin/Fak/Src-mediated regulation of cell survival and anoikis in human intestinal epithelial crypt cells: selective engagement and roles of PI3-K isoform complexes.Apoptosis. 2012 Jun;17(6):566-78. doi: 10.1007/s10495-012-0713-6. Apoptosis. 2012. PMID: 22402981 Free PMC article.
-
Production of a Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vaccine Antigen Using Suspension-Adapted BHK-21 Cells in a Bioreactor.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 May 13;9(5):505. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9050505. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34068378 Free PMC article.
-
PU.1 inhibition attenuates atrial fibrosis and atrial fibrillation vulnerability induced by angiotensin-II by reducing TGF-β1/Smads pathway activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jul;25(14):6746-6759. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16678. Epub 2021 Jun 15. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34132026 Free PMC article.
-
The vitronectin RGD motif regulates TGF-β-induced alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):L1206-17. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00424.2015. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27106291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J. C. and Watt, F. M. (1989). Fibronectin inhibits the terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes. Nature 340, 307-309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

