SV40 DNA replication: from the A gene to a nanomachine
- PMID: 19101707
- PMCID: PMC2718763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.11.038
SV40 DNA replication: from the A gene to a nanomachine
Abstract
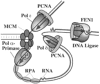
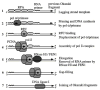
Duplication of the simian virus 40 (SV40) genome is the best understood eukaryotic DNA replication process to date. Like most prokaryotic genomes, the SV40 genome is a circular duplex DNA organized in a single replicon. This small viral genome, its association with host histones in nucleosomes, and its dependence on the host cell milieu for replication factors and precursors led to its adoption as a simple and powerful model. The steps in replication, the viral initiator, the host proteins, and their mechanisms of action were initially defined using a cell-free SV40 replication reaction. Although our understanding of the vastly more complex host replication fork is advancing, no eukaryotic replisome has yet been reconstituted and the SV40 paradigm remains a point of reference. This article reviews some of the milestones in the development of this paradigm and speculates on its potential utility to address unsolved questions in eukaryotic genome maintenance.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Single-molecule characterization of SV40 replisome and novel factors: human FPC and Mcm10.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 27;52(15):8880-8896. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae565. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38967018 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro replication of DNA containing either the SV40 or the polyoma origin.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Dec 15;317(1187):439-53. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1987.0071. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987. PMID: 2894681
-
Functional interactions between SV40 T antigen and other replication proteins at the replication fork.J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11008-17. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8098707
-
The initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1997;32(6):503-68. doi: 10.3109/10409239709082001. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9444478 Review.
-
The replication functions of SV40 T antigen are regulated by phosphorylation.Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):735-8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90179-i. Cell. 1990. PMID: 2160857 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Closing the DNA replication cycle: from simple circular molecules to supercoiled and knotted DNA catenanes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Aug 22;47(14):7182-7198. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz586. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31276584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SV40 T antigen helicase domain regions responsible for oligomerisation regulate Okazaki fragment synthesis initiation.FEBS Open Bio. 2022 Mar;12(3):649-663. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13373. Epub 2022 Feb 7. FEBS Open Bio. 2022. PMID: 35073603 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient propagation of archetype BK and JC polyomaviruses.Virology. 2012 Jan 20;422(2):235-41. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.10.026. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Virology. 2012. PMID: 22099377 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Replication Origins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1042:43-59. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-6955-0_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29357052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of large T antigen regulates merkel cell polyomavirus replication.Cancers (Basel). 2014 Jul 8;6(3):1464-86. doi: 10.3390/cancers6031464. Cancers (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25006834 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

