The neuronal connexin36 interacts with and is phosphorylated by CaMKII in a way similar to CaMKII interaction with glutamate receptors
- PMID: 19095792
- PMCID: PMC2605416
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805408105
The neuronal connexin36 interacts with and is phosphorylated by CaMKII in a way similar to CaMKII interaction with glutamate receptors
Abstract
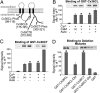
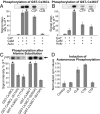
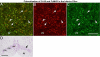
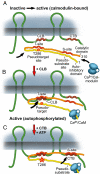
Electrical synapses can undergo activity-dependent plasticity. The calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) appears to play a critical role in this phenomenon, but the underlying mechanisms of how CaMKII affects the neuronal gap junction protein connexin36 (Cx36) are unknown. Here we demonstrate effective binding of (35)S-labeled CaMKII to 2 juxtamembrane cytoplasmic domains of Cx36 and in vitro phosphorylation of this protein by the kinase. Both domains reveal striking similarities with segments of the regulatory subunit of CaMKII, which include the pseudosubstrate and pseudotarget sites of the kinase. Similar to the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor both Cx36 binding sites exhibit phosphorylation-dependent interaction and autonomous activation of CaMKII. CaMKII and Cx36 were shown to be significantly colocalized in the inferior olive, a brainstem nucleus highly enriched in electrical synapses, indicating physical proximity of these proteins. In analogy to the current notion of NR2B interaction with CaMKII, we propose a model that provides a mechanistic framework for CaMKII and Cx36 interaction at electrical synapses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tubulin-Dependent Transport of Connexin-36 Potentiates the Size and Strength of Electrical Synapses.Cells. 2019 Sep 25;8(10):1146. doi: 10.3390/cells8101146. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31557934 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Calmodulin and CaMKII in Cx36 Plasticity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 25;22(9):4473. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094473. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33922931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Convergent NMDA receptor-Pannexin1 signaling pathways regulate the interaction of CaMKII with Connexin-36.Commun Biol. 2021 Jun 8;4(1):702. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02230-x. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34103655 Free PMC article.
-
Variability of distribution of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent kinase II at mixed synapses on the mauthner cell: colocalization and association with connexin 35.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 14;30(28):9488-99. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4466-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20631177 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-driven postsynaptic translocation of CaMKII.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Dec;26(12):645-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2005.10.003. Epub 2005 Oct 25. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16253351 Review.
Cited by
-
Active roles of electrically coupled bipolar cell network in the adult retina.J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 7;30(27):9260-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1590-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20610761 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreceptor coupling is controlled by connexin 35 phosphorylation in zebrafish retina.J Neurosci. 2009 Dec 2;29(48):15178-86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3517-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19955370 Free PMC article.
-
Localized Calcium Signaling and the Control of Coupling at Cx36 Gap Junctions.eNeuro. 2020 Apr 17;7(2):ENEURO.0445-19.2020. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0445-19.2020. Print 2020 Mar/Apr. eNeuro. 2020. PMID: 32179580 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of magnesium-dependent synaptic plasticity at electrical synapses formed by connexin36.Nat Commun. 2014 Aug 19;5:4667. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5667. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25135336 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin dependent protein kinase increases conductance at gap junctions formed by the neuronal gap junction protein connexin36.Brain Res. 2012 Dec 3;1487:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.06.058. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22796294 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

