Sensing voltage across lipid membranes
- PMID: 19092925
- PMCID: PMC2629456
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07620
Sensing voltage across lipid membranes
Abstract
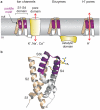
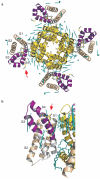
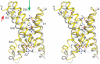
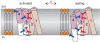
The detection of electrical potentials across lipid bilayers by specialized membrane proteins is required for many fundamental cellular processes such as the generation and propagation of nerve impulses. These membrane proteins possess modular voltage-sensing domains, a notable example being the S1-S4 domains of voltage-activated ion channels. Ground-breaking structural studies on these domains explain how voltage sensors are designed and reveal important interactions with the surrounding lipid membrane. Although further structures are needed to understand the conformational changes that occur during voltage sensing, the available data help to frame several key concepts that are fundamental to the mechanism of voltage sensing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural interactions between lipids, water and S1-S4 voltage-sensing domains.J Mol Biol. 2012 Nov 2;423(4):632-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.07.015. Epub 2012 Jul 31. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22858867 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and hydration of membranes embedded with voltage-sensing domains.Nature. 2009 Nov 26;462(7272):473-9. doi: 10.1038/nature08542. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19940918 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage Sensing in Membranes: From Macroscopic Currents to Molecular Motions.J Membr Biol. 2015 Jun;248(3):419-30. doi: 10.1007/s00232-015-9805-x. Epub 2015 May 14. J Membr Biol. 2015. PMID: 25972106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between lipids and voltage sensor paddles detected with tarantula toxins.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Oct;16(10):1080-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1679. Epub 2009 Sep 27. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19783984 Free PMC article.
-
A complicated complex: Ion channels, voltage sensing, cell membranes and peptide inhibitors.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Jul 13;679:35-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.04.030. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 29684532 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and biophysical basis of glutamate and trace metal modulation of voltage-gated Ca(v)2.3 calcium channels.J Gen Physiol. 2012 Mar;139(3):219-34. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201110699. J Gen Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22371363 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the S5-pore-S6 domain to the gating characteristics of the cation channels TRPM2 and TRPM8.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 27;285(35):26806-26814. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.109975. Epub 2010 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20587417 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids in neurodegeneration.Neuromolecular Med. 2010 Dec;12(4):301-5. doi: 10.1007/s12017-010-8135-5. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Neuromolecular Med. 2010. PMID: 20737248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Voltage Regulation Mechanism of the Pore-Forming Toxin Lysenin.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Aug 17;10(8):334. doi: 10.3390/toxins10080334. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30126104 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning voltage-gated channel activity and cellular excitability with a sphingomyelinase.J Gen Physiol. 2013 Oct;142(4):367-80. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201310986. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Gen Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24043861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noda M, et al. Expression of functional sodium channels from cloned cDNA. Nature. 1986;322:826–8. - PubMed
-
- Tanabe T, et al. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987;328:313–8. - PubMed
-
- Tempel BL, Papazian DM, Schwarz TL, Jan YN, Jan LY. Sequence of a probable potassium channel component encoded at Shaker locus of Drosophila. Science. 1987;237:770–5. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, et al. X-ray structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature. 2003;423:33–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

