Induction of microRNA-221 by platelet-derived growth factor signaling is critical for modulation of vascular smooth muscle phenotype
- PMID: 19088079
- PMCID: PMC2635044
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808788200
Induction of microRNA-221 by platelet-derived growth factor signaling is critical for modulation of vascular smooth muscle phenotype
Abstract
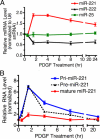
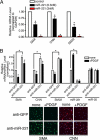
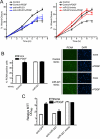
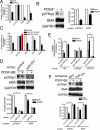
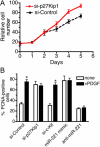
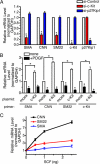
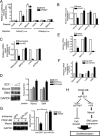
The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling pathway is a critical regulator of animal development and homeostasis. Activation of the PDGF pathway leads to neointimal proliferative responses to artery injury; it promotes a switch of vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMC) to a less contractile phenotype by inhibiting the SMC-specific gene expression and increasing the rate of proliferation and migration. The molecular mechanism for these pleiotropic effects of PDGFs has not been fully described. Here, we identify the microRNA-221 (miR-221), a small noncoding RNA, as a modulator of the phenotypic change of vSMCs in response to PDGF signaling. We demonstrate that miR-221 is transcriptionally induced upon PDGF treatment in primary vSMCs, leading to down-regulation of the targets c-Kit and p27Kip1. Down-regulation of p27Kip1 by miR-221 is critical for PDGF-mediated induction of cell proliferation. Additionally, decreased c-Kit causes inhibition of SMC-specific contractile gene transcription by reducing the expression of Myocardin (Myocd), a potent SMC-specific nuclear coactivator. Our study demonstrates that PDGF signaling, by modulating the expression of miR-221, regulates two critical determinants of the vSMC phenotype; they are SMC gene expression and cell proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-638 is highly expressed in human vascular smooth muscle cells and inhibits PDGF-BB-induced cell proliferation and migration through targeting orphan nuclear receptor NOR1.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Jul 1;99(1):185-93. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt082. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23554459 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardin regulates vascular response to injury through miR-24/-29a and platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Oct;33(10):2355-65. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.301000. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23825366
-
miR-15b induced by platelet-derived growth factor signaling is required for vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.BMB Rep. 2013 Nov;46(11):550-4. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.11.057. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 24152911 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardin/microRNA-30a/Beclin1 signaling controls the phenotypic modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating autophagy.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 8;13(2):121. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04588-0. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35136037 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics and miRNA emerge as key regulators of smooth muscle cell phenotype and function.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Feb;26(1):75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 22800879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells in intimal hyperplasia, an update.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 4;13:1081881. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1081881. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36685215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized phospholipids stimulate production of stem cell factor via NRF2-dependent mechanisms.Angiogenesis. 2018 May;21(2):229-236. doi: 10.1007/s10456-017-9590-5. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Angiogenesis. 2018. PMID: 29330760 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs: the "dark matter" of cardiovascular pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Oct 9;14(10):19987-20018. doi: 10.3390/ijms141019987. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24113581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA expression profile and functional analysis reveal their roles in contact inhibition and its disruption switch of rat vascular smooth muscle cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 May;39(5):885-892. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.6. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29698390 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Regulating Plaque Progression and Remodeling of Extracellular Matrix in Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 8;23(22):13731. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213731. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430208 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

