Level, phenotype and activation status of CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus and/or hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 19076827
- PMCID: PMC2665677
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03797.x
Level, phenotype and activation status of CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus and/or hepatitis C virus
Abstract
CD4(+) regulatory T (T(reg)) cells have been involved in impaired immunity and persistence of viral infections. Herein, we report the level, phenotype and activation status of T(reg) cells in patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and/or hepatitis C virus (HCV). Expression of CD25, CD45RA, CD27, CD127 and CD38 was assessed on these cells using polychromatic flow cytometry in 20 healthy controls, 20 HIV-monoinfected, 20 HCV-monoinfected and 31 HIV/HCV-co-infected patients. T(reg) cells were defined as CD4(+)forkhead box P3 (FoxP3)(+). The percentage of T(reg) cells was increased significantly in HIV patients compared with controls. Moreover, there was a significant inverse correlation between CD4 counts and T(reg) cell levels. Fewer than 50% of T(reg) cells expressed CD25, with differences in terms of CD127 expression between CD25(+) and CD25((-)) T(reg) cells. CD4(+)Foxp3(+) T(reg) cells displayed predominantly a central memory phenotype (CD45RA(-)CD27(+)), without differences between patients and healthy controls. Activated T(reg) cells were increased in HIV patients, particularly considering the central memory subset. In summary, HIV infection, but not HCV, induces an up-regulation of highly activated T(reg) cells, which increases in parallel with CD4 depletion. Hypothetically, this might contribute to the accelerated course of HCV-related liver disease in HIV-immunosuppressed patients.
Figures

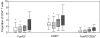

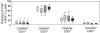
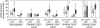
Similar articles
-
CD4+CD25+CD127- assessment as a surrogate phenotype for FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in HIV-1 infected viremic and aviremic subjects.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2013 Jan-Feb;84(1):50-4. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.21047. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2013. PMID: 23019018
-
FOXP3 expressing CD127lo CD4+ T cells inversely correlate with CD38+ CD8+ T cell activation levels in primary HIV-1 infection.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Feb;83(2):254-62. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0507281. Epub 2007 Nov 2. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 17982112
-
F protein increases CD4+CD25+ T cell population in patients with chronic hepatitis C.Pathog Dis. 2015 Jun;73(4):ftv022. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv022. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 25862675
-
Mechanisms of impaired regulation by CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells in human autoimmune diseases.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Dec;10(12):849-59. doi: 10.1038/nri2889. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21107346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Divergent contributions of regulatory T cells to the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis C.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Jul;9(7):1569-76. doi: 10.4161/hv.24726. Epub 2013 May 31. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23732899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early and long-lasting alteration of effector CD45RA(-)Foxp3(high) regulatory T-cell homeostasis during HIV infection.J Infect Dis. 2012 May 15;205(10):1510-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis235. Epub 2012 Mar 28. J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22457280 Free PMC article.
-
Increased frequency of regulatory T cells accompanies increased immune activation in rectal mucosae of HIV-positive noncontrollers.J Virol. 2011 Nov;85(21):11422-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05608-11. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21880771 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead box protein 3(+) regulatory T cells and Helios(+) subset in perinatally acquired HIV.Clin Exp Immunol. 2015 Apr;180(1):108-17. doi: 10.1111/cei.12560. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25425428 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Persistence of Protective Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titers after Successful Double-Dose Hepatitis B Virus Rescue Vaccination in HIV-Infected Patients.Gut Liver. 2012 Jan;6(1):86-91. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2012.6.1.86. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Gut Liver. 2012. PMID: 22375176 Free PMC article.
-
HCV viraemia associates with NK cell activation and dysfunction in antiretroviral therapy-treated HIV/HCV-co-infected subjects.J Viral Hepat. 2017 Oct;24(10):865-876. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12714. Epub 2017 May 11. J Viral Hepat. 2017. PMID: 28419653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schmitz J, Schmitz JE, Kuroda MJ, et al. Control of viremia in simian immunodeficiency virus infection by CD8+ lymphocytes. Science. 1999;283:857–60. - PubMed
-
- Shankar P, Russo M, Harnisch B, Patterson M, Skolnik P, Lieberman J. Impaired function of circulating HIV-specific CD8+ T-cells in chronic HIV infection. Blood. 2000;96:3094–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

