Single virus detection from the reactive shift of a whispering-gallery mode
- PMID: 19075225
- PMCID: PMC2603258
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808988106
Single virus detection from the reactive shift of a whispering-gallery mode
Abstract
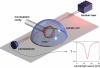
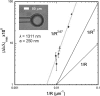
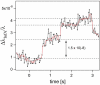
We report the label-free, real-time optical detection of Influenza A virus particles. Binding of single virions is observed from discrete changes in the resonance frequency/wavelength of a whispering-gallery mode excited in a microspherical cavity. We find that the magnitude of the discrete wavelength-shift signal can be sufficiently enhanced by reducing the microsphere size. A reactive sensing mechanism with inverse dependence on mode volume is confirmed in experiments with virus-sized polystyrene nanoparticles. By comparing the electromagnetic theory for this reactive effect with experiments, the size and mass ( approximately 5.2 x 10(-16) g) of a bound virion are determined directly from the optimal resonance shift.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detecting single viruses and nanoparticles using whispering gallery microlasers.Nat Nanotechnol. 2011 Jun 26;6(7):428-32. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.99. Nat Nanotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21706025
-
Single virus and nanoparticle size spectrometry by whispering-gallery-mode microcavities.Opt Express. 2011 Aug 15;19(17):16195-206. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.016195. Opt Express. 2011. PMID: 21934982
-
Label-free detection of virus-like particles employing rotationally symmetric nanowire array based whispering gallery and quasi-whispering gallery resonant modes onto a silicon platform.Opt Express. 2021 Aug 2;29(16):25745-25761. doi: 10.1364/OE.432064. Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 34614897
-
Optical microcavity: sensing down to single molecules and atoms.Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(2):1972-91. doi: 10.3390/s110201972. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Sensors (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22319393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Label-Free Biological and Chemical Sensing Using Whispering Gallery Mode Optical Resonators: Past, Present, and Future.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Mar 8;17(3):540. doi: 10.3390/s17030540. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28282881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomolecular analysis with microring resonators: applications in multiplexed diagnostics and interaction screening.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013 Oct;17(5):818-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23871688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single Nanoparticle Detection Using Far-field Emission of Photonic Molecule around the Exceptional Point.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 7;5:11912. doi: 10.1038/srep11912. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26149067 Free PMC article.
-
A fiber-tip label-free biological sensing platform: a practical approach toward in-vivo sensing.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Jan 9;15(1):1168-81. doi: 10.3390/s150101168. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25585104 Free PMC article.
-
The Detection of Helicobacter hepaticus Using Whispering-Gallery Mode Microcavity Optical Sensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2015 Aug 7;5(3):562-76. doi: 10.3390/bios5030562. Biosensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26262647 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid genetic screening with high quality factor metasurfaces.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2021 Oct 15:arXiv:2110.07862v2. ArXiv. 2021. Update in: Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 26;14(1):4486. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39721-w. PMID: 34671699 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ewald P.W. In: The Next Fifty Years. Brockman J, editor. New York: Vintage Books; 2002. pp. 289–301.
-
- Arnold S, Khoshsima M, Teraoka I, Holler S, Vollmer F. Shift of whispering gallery modes in microspheres by protein adsorption. Opt Lett. 2003;28:272–274. - PubMed
-
- Arnold S, Ramjit R, Keng D, Kolchenko V, Teraoka I. Microparticle photophysics illuminates viral biosensing. Faraday Discuss. 2008;137:65–85. - PubMed
-
- Ignatovich FV, Novotny L. Real-time and background-free detection of nanoscale particles. Phys Rev Lett. 2006;96:0139011–0139014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

