Robust antiviral efficacy upon administration of a nucleoside analog to hepatitis C virus-infected chimpanzees
- PMID: 19075052
- PMCID: PMC2650549
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01032-08
Robust antiviral efficacy upon administration of a nucleoside analog to hepatitis C virus-infected chimpanzees
Abstract
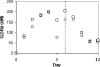
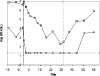
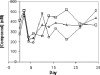
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infects an estimated 170 million individuals worldwide and is associated with an increased incidence of liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Currently approved therapies to treat HCV infection consist of combinations of pegylated alpha interferon and ribavirin which result in a sustained viral response in 40 to 60% of patients. Efforts to develop improved therapies include the development of direct inhibitors of virally encoded enzymes such as the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. A nucleoside analog, 2'-C-methyl-7-deaza-adenosine (MK-0608), has been shown to inhibit viral RNA replication in the subgenomic HCV genotype 1b replicon, with a 50% effective concentration (EC(50)) of 0.3 microM (EC(90) = 1.3 microM). To determine efficacy in vivo, MK-0608 was administered to HCV-infected chimpanzees, resulting in dose- and time-dependent decreases in plasma viral loads. In separate experiments, chimpanzees dosed for 7 days with MK-0608 at 0.2 and 2 mg per kg of body weight per day by intravenous administration experienced average reductions in viral load of 1.0 and >5 log(10) IU/ml, respectively. Two other HCV-infected chimpanzees received daily doses of 1 mg MK-0608 per kg via oral administration. After 37 days of oral dosing, one chimpanzee with a high starting viral load experienced a reduction in viral load of 4.6 log(10), and the viral load in the other chimpanzee fell below the limit of quantification (LOQ) of the HCV TaqMan assay (20 IU/ml). Importantly, viral load remained below the LOQ throughout the duration of dosing and for at least 12 days after dosing ended. The results demonstrate a robust antiviral effect on the administration of MK-0608 to HCV-infected chimpanzees.
Figures
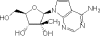


Similar articles
-
Antiviral efficacy upon administration of a HepDirect prodrug of 2'-C-methylcytidine to hepatitis C virus-infected chimpanzees.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Aug;55(8):3854-60. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01152-10. Epub 2011 May 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21628542 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of a potent hepatitis C virus polymerase inhibitor in the chimpanzee model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Dec;51(12):4290-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00723-07. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17908950 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained viral response in a hepatitis C virus-infected chimpanzee via a combination of direct-acting antiviral agents.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Feb;55(2):937-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00990-10. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21115793 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleoside analog inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006 Mar;6(1):17-29. doi: 10.2174/187152606776056698. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16787301 Review.
-
R-1626, a specific oral NS5B polymerase inhibitor of hepatitis C virus.IDrugs. 2008 Oct;11(10):738-49. IDrugs. 2008. PMID: 18828074 Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse Systems to Model Hepatitis C Virus Treatment and Associated Resistance.Viruses. 2016 Jun 22;8(6):176. doi: 10.3390/v8060176. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27338446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infectivity in chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) of plasma collected before HCV RNA detectability by FDA-licensed assays: implications for transfusion safety and HCV infection outcomes.Blood. 2012 Jun 28;119(26):6326-34. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-393637. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22498743 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleoside inhibitors of tick-borne encephalitis virus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Sep;59(9):5483-93. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00807-15. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26124166 Free PMC article.
-
Competing interests during the key N-glycosylation of 6-chloro-7-deaza-7-iodopurine for the synthesis of 7-deaza-2'-methyladenosine using Vorbrüggen conditions.Front Chem. 2023 Mar 23;11:1163486. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1163486. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37035111 Free PMC article.
-
Finally sofosbuvir: an oral anti-HCV drug with wide performance capability.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2014 Dec 8;7:387-98. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S52629. eCollection 2014. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2014. PMID: 25540594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afdahl, N., C. O'Brien, E. Godofsky, M. Rodriguez-Torres, S. C. Pappas, P. Pockros, E. Lwitz, N. Bzowej, V. Rustgi, M. Sulkowski, and K. Sherman. 2006. Valopicitabine (NM283), alone or with peg-interferon, compared to peg-interferon/ribavirin (pegIFN/RBV) re-treatment in hepatitis C patients with prior non-response to pegIFN/RBV: week 24 results. J. Hepatol. 44(Suppl. 2):S19.. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu, P. L., M. Bos, Y. Bousquet, G. Fazal, J. Gauthier, J. Gillard, S. Goulet, S. LaPlante, M. A. Poupart, S. Lefebvre, G. McKercher, C. Pellerin, V. Austel, and G. Kukolj. 2004. Non-nucleoside inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase: discovery and preliminary SAR of benzimidazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14:119-124. - PubMed
-
- Bukh, J., X. Forns, S. U. Emerson, and R. H. Purcell. 2001. Studies of hepatitis C virus in chimpanzees and their importance for vaccine development. Intervirology 44:132-142. - PubMed
-
- Carroll, S. S., J. E. Tomassini, M. Bosserman, K. Getty, M. W. Stahlhut, A. B. Eldrup, B. Bhat, D. Hall, A. L. Simcoe, R. LaFemina, C. A. Rutkowski, B. Wolanski, Z. Yang, G. Migliaccio, R. De Francesco, L. C. Kuo, M. MacCoss, and D. B. Olsen. 2003. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus RNA replication by 2′-modified nucleoside analogs. J. Biol. Chem. 278:11979-11984. - PubMed
-
- Chan, L., O. Pereira, T. J. Reddy, S. K. Das, C. Poisson, M. Courchesne, M. Proulx, A. Siddiqui, C. G. Yannopoulos, N. Nguyen-Ba, C. Roy, D. Nasturica, C. Moinet, R. Bethell, M. Hamel, L. L'Heureux, M. David, O. Nicolas, P. Courtemanche-Asselin, S. Brunette, D. Bilimoria, and J. Bedard. 2004. Discovery of thiophene-2-carboxylic acids as potent inhibitors of HCV NS5B polymerase and HCV subgenomic RNA replication. Part 2: tertiary amides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14:797-800. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

