Aging and cancer resistance in lymphoid progenitors are linked processes conferred by p16Ink4a and Arf
- PMID: 19056891
- PMCID: PMC2593609
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1715808
Aging and cancer resistance in lymphoid progenitors are linked processes conferred by p16Ink4a and Arf
Abstract
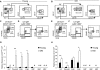
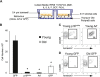
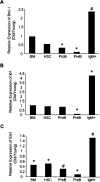
Lymphoid progenitors exhibit severe growth defects during aging while myelopoiesis is relatively unperturbed. These effects are due in part to the preferential expression of p16(Ink4a) and Arf in aged lymphoid progenitors. Their increased expression contributes to reduced growth and survival of lymphoid progenitors and makes them refractory to malignant transformation. Down-regulation of p16(Ink4a) and Arf in aged lymphoid progenitors reverted the senescent phenotype and restored susceptibility to transformation. These data provide a molecular explanation for the preferential effects of aging on lymphopoiesis, suggest that inhibiting p16(Ink4a) and Arf expression can rejuvenate B lymphopoiesis, and link aging and cancer resistance.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential effects of p19(Arf) and p16(Ink4a) loss on senescence of murine bone marrow-derived preB cells and macrophages.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Aug 14;98(17):9654-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.171217498. Epub 2001 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11481442 Free PMC article.
-
p16(Ink4a) interferes with Abelson virus transformation by enhancing apoptosis.J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(7):3304-11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3304-3311.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15016851 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of primary cultured mouse hepatic tumor cells to cellular senescence despite expression of p16(Ink4a), p19(Arf), p53, and p21(Waf1/Cip1).Mol Carcinog. 2001 Sep;32(1):9-18. doi: 10.1002/mc.1059. Mol Carcinog. 2001. PMID: 11568971
-
The INK4a/ARF locus and melanoma.Oncogene. 2003 May 19;22(20):3092-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206461. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12789286 Review.
-
Genetic Alterations in the INK4a/ARF Locus: Effects on Melanoma Development and Progression.Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 15;10(10):1447. doi: 10.3390/biom10101447. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33076392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring tumorigenesis and senescence in vivo with a p16(INK4a)-luciferase model.Cell. 2013 Jan 17;152(1-2):340-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.010. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23332765 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor-7 partially reverses murine thymocyte progenitor aging by repression of Ink4a.Blood. 2012 Jun 14;119(24):5715-21. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-400002. Epub 2012 May 3. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22555975 Free PMC article.
-
Do haematopoietic stem cells age?Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 Mar;20(3):196-202. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0236-2. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31740804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A quantitative model for age-dependent expression of the p16INK4a tumor suppressor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 29;106(39):16562-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904405106. Epub 2009 Sep 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19805338 Free PMC article.
-
Aging-associated changes in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis: what's the connection?Aging (Albany NY). 2011 Jun;3(6):643-56. doi: 10.18632/aging.100351. Aging (Albany NY). 2011. PMID: 21765201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akashi K., Traver D., Miyamoto T., Weissman I.L. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature. 2000;404:193–197. - PubMed
-
- Jacobs J.J., Kieboom K., Marino S., DePinho R.A., van Lohuizen M. The oncogene and Polycomb-group gene bmi-1 regulates cell proliferation and senescence through the ink4a locus. Nature. 1999;397:164–168. - PubMed
-
- Janzen V., Forkert R., Fleming H.E., Saito Y., Waring M.T., Dombkowski D.M., Cheng T., DePinho R.A., Sharpless N.E., Scadden D.T. Stem-cell ageing modified by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16INK4a. Nature. 2006;443:421–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
