Identification of precursor transcripts for 6 novel miRNAs expands the diversity on the genomic organisation and expression of miRNA genes in rice
- PMID: 19055717
- PMCID: PMC2607281
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-8-123
Identification of precursor transcripts for 6 novel miRNAs expands the diversity on the genomic organisation and expression of miRNA genes in rice
Abstract
Background: The plant miRNAs represent an important class of endogenous small RNAs that guide cleavage of an mRNA target or repress its translation to control development and adaptation to stresses. MiRNAs are nuclear-encoded genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II, producing a primary precursor that is subsequently processed by DCL1 an RNase III Dicer-like protein. In rice hundreds of miRNAs have been described or predicted, but little is known on their genes and precursors which are important criteria to distinguish them from siRNAs. Here we develop a combination of experimental approaches to detect novel miRNAs in rice, identify their precursor transcripts and genes and predict or validate their mRNA targets.
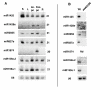
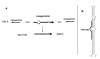
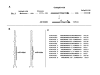
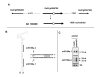
Results: We produced four cDNA libraries from small RNA fractions extracted from distinct rice tissues. By in silico analysis we selected 6 potential novel miRNAs, and confirmed that their expression requires OsDCL1. We predicted their targets and used 5'RACE to validate cleavage for three of them, targeting a PPR, an SPX domain protein and a GT-like transcription factor respectively. In addition, we identified precursor transcripts for the 6 miRNAs expressed in rice, showing that these precursors can be efficiently processed using a transient expression assay in transfected Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Most interestingly, we describe two precursors producing tandem miRNAs, but in distinct arrays. We focus on one of them encoding osa-miR159a.2, a novel miRNA produced from the same stem-loop structure encoding the conserved osa-miR159a.1. We show that this dual osa-miR159a.2-osa-miR159a.1 structure is conserved in distant rice species and maize. Finally we show that the predicted mRNA target of osa-miR159a.2 encoding a GT-like transcription factor is cleaved in vivo at the expected site.
Conclusion: The combination of approaches developed here identified six novel miRNAs expressed in rice which can be clearly distinguished from siRNAs. Importantly, we show that two miRNAs can be produced from a single precursor, either from tandem stem-loops or tandemly arrayed in a single stem-loop. This suggests that processing of these precursors could be an important regulatory step to produce one or more functional miRNAs in plants and perhaps coordinate cleavage of distinct targets in the same plant tissue.
Figures




Similar articles
-
microRNAs targeting DEAD-box helicases are involved in salinity stress response in rice (Oryza sativa L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Oct 8;12:183. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-183. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23043463 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis for discovery of rice microRNAs reveals natural antisense microRNAs (nat-miRNAs).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Mar 25;105(12):4951-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708743105. Epub 2008 Mar 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18353984 Free PMC article.
-
The Phaseolus vulgaris miR159a precursor encodes a second differentially expressed microRNA.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;80(1):103-15. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9847-0. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22083131
-
MicroRNA-mediated host defense mechanisms against pathogens and herbivores in rice: balancing gains from genetic resistance with trade-offs to productivity potential.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jul 18;22(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03723-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35850632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA stem-loops: to be or not to be cleaved by RNAse III.RNA. 2007 Apr;13(4):457-62. doi: 10.1261/rna.366507. Epub 2007 Feb 13. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17299129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary conservation of nested MIR159 structural microRNA genes and their promoter characterization in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jul 26;13:948751. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.948751. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35958213 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal small RNA transcriptome profiling unraveled partitioned miRNA expression in developing maize endosperms between reciprocal crosses.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Sep 15;6:744. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00744. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26442057 Free PMC article.
-
PMRD: plant microRNA database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(Database issue):D806-13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp818. Epub 2009 Oct 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19808935 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterisation of microRNAs and their target genes in phosphate-starved Nicotiana benthamiana by small RNA deep sequencing and 5'RACE analysis.BMC Genomics. 2018 Dec 17;19(1):940. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5258-9. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30558535 Free PMC article.
-
Developmentally regulated expression and complex processing of barley pri-microRNAs.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jan 16;14:34. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-34. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23324356 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

