Efficacy and toxicity of methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy versus MTX combination therapy with non-biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 19054823
- PMCID: PMC2689526
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2008.099861
Efficacy and toxicity of methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy versus MTX combination therapy with non-biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy compared with MTX combination with non-biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
Method: A systematic review of randomised trials comparing MTX alone and in combination with other non-biological DMARDs was carried out. Trials were identified in Medline, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library and ACR/EULAR meeting abstracts. Primary outcomes were withdrawals for adverse events or lack of efficacy.
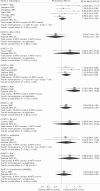
Results: A total of 19 trials (2025 patients) from 6938 citations were grouped by the type of patients randomised. Trials in DMARD naive patients showed no significant advantage of the MTX combination versus monotherapy; withdrawals for lack of efficacy or toxicity were similar in both groups (relative risk (RR) = 1.16; 95% CI 0.70 to 1.93). Trials in MTX or non-MTX DMARD inadequate responder patients also showed no difference in withdrawal rates between the MTX combo versus mono groups (RR = 0.86; 95% CI 0.49 to 1.51 and RR = 0.75; 95% CI 0.41 to 1.35), but in one study the specific combination of MTX with sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine showed a better efficacy/toxicity ratio than MTX alone with RR = 0.3 (95% CI 0.14 to 0.65). Adding leflunomide to MTX non-responders improved efficacy but increased the risk of gastrointestinal side effects and liver toxicity. Withdrawals for toxicity were most significant with ciclosporin and azathioprine combinations.
Conclusion: In DMARD naive patients the balance of efficacy/toxicity favours MTX monotherapy. In DMARD inadequate responders the evidence is inconclusive. Trials are needed that compare currently used MTX doses and combination therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Methotrexate monotherapy versus methotrexate combination therapy with non-biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Apr 14;2010(4):CD008495. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008495. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20393970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD004525. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004525.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis of the efficacy and toxicity of combining disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis based on patient withdrawal.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 Nov;44(11):1414-21. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kei031. Epub 2005 Jul 19. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. PMID: 16030080 Review.
-
Methotrexate monotherapy and methotrexate combination therapy with traditional and biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis: A network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 29;2016(8):CD010227. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010227.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27571502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triple Oral Therapy Versus Antitumor Necrosis Factor Plus Methotrexate (MTX) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response to MTX: A Systematic Literature Review.J Rheumatol. 2017 Jun;44(6):773-779. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.160643. Epub 2017 Apr 15. J Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28412710
Cited by
-
Comparative effectiveness of treatment with the first TNF antagonist in monotherapy, the first TNF antagonist plus one conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug, and the first TNF antagonist plus two or more conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Nov 8;18(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1137-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27821150 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Therapy for Psoriasis with Methotrexate and Other Oral Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: A Systematic Review.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Apr;13(4):891-909. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-00903-5. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 36943580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug interaction between methotrexate and salazosulfapyridine in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2017 Jan 19;3:7. doi: 10.1186/s40780-017-0073-z. eCollection 2017. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2017. PMID: 28116118 Free PMC article.
-
Leflunomide increases the risk of silent liver fibrosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Oct 29;14(5):R232. doi: 10.1186/ar4075. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 23107811 Free PMC article.
-
Methotrexate monotherapy versus methotrexate combination therapy with non-biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Apr 14;2010(4):CD008495. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008495. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20393970 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Möttönen T, Hannonen P, Leirisalo-Repo M, Nissilä M, Kautiainen H, Korpela M, et al. Comparison of combination therapy with single-drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised trial Lancet 1999;353:1568–73 - PubMed
-
- Goekoop-Ruiterman YPM, de Vries-Bouwstra J, Allaart C, van Zeben D, Kerstens PJSM, Hazes J, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt study): a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:3381–90 - PubMed
-
- Goekoop-Ruiterman YPM, de Vries-Bouwstra J, Allaart C, van Zeben D, Kerstens PJSM, Hazes J, et al. Comparison of treatment strategies in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2007;146:406–15 - PubMed
-
- Marchesoni A, Battafarano N, Arreghini M, Gallazzi M, Tosi S. Radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: a 12-month randomized controlled study comparing the combination of cyclosporin and methotrexate with methotrexate alone. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003;42:1545–9 - PubMed
-
- Tascioglu F, Oner C, Armagan O. Comparison of low dose methotrexate and combination therapy with methotrexate and sulphasalazine in the treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Med Rehab 2003;14:142–9
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
