Mediobasal hypothalamic p70 S6 kinase 1 modulates the control of energy homeostasis
- PMID: 19041762
- PMCID: PMC2637401
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.10.004
Mediobasal hypothalamic p70 S6 kinase 1 modulates the control of energy homeostasis
Abstract
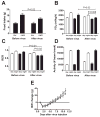
p70 S6 kinase 1 (S6K) is a major downstream effector of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), primarily implicated in the control of protein synthesis, cell growth, and proliferation. Here we demonstrate that specific bidirectional molecular targeting of mediobasal hypothalamic (MBH) S6K activity in rats is sufficient to significantly alter food intake, body weight, hypothalamic orexigenic neuropeptide expression, hypothalamic leptin sensitivity, and the metabolic and feeding responses to a fast. In addition, adenoviral-mediated constitutive activation of MBH S6K improved cold tolerance and protected against high-fat diet-induced overeating, fat deposition, and insulin resistance. Our results provide direct evidence that MBH S6K activity bidirectionally drives behavioral and metabolic determinants of energy balance and promote the assessment of MBH S6K activity as a therapeutic target in metabolic diseases.
Figures

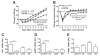

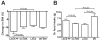
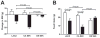
Similar articles
-
Activation of hypothalamic S6 kinase mediates diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance in rats.J Clin Invest. 2008 Aug;118(8):2959-68. doi: 10.1172/JCI34277. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18618016 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of insulin signaling and adipogenesis by rapamycin: effect on phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase vs eIF4E-BP1.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004 Feb;28(2):191-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802554. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004. PMID: 14970836
-
A possible linkage between AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway.Genes Cells. 2003 Jan;8(1):65-79. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2003.00615.x. Genes Cells. 2003. PMID: 12558800
-
TOR action in mammalian cells and in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004;279:115-38. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-18930-2_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14560955 Review.
-
[Research progress of p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase inhibitors].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Mar;50(3):261-71. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26118103 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Functional organization of neuronal and humoral signals regulating feeding behavior.Annu Rev Nutr. 2013;33:1-21. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071812-161125. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Annu Rev Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23642202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central leucine sensing in the control of energy homeostasis.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2013 Mar;42(1):81-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2012.12.001. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2013. PMID: 23391241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Kinases in Obesity, and the Kinase-Targeted Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:199-229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287853 Review.
-
Reviewing the Effects of L-Leucine Supplementation in the Regulation of Food Intake, Energy Balance, and Glucose Homeostasis.Nutrients. 2015 May 22;7(5):3914-37. doi: 10.3390/nu7053914. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 26007339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Elevated Branched-Chain Amino Acids in the Effects of Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy to Reduce Weight and Improve Glucose Regulation.Cell Rep. 2020 Oct 13;33(2):108239. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108239. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33053352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asaki C, Usuda N, Nakazawa A, Kametani K, Suzuki T. Localization of translational components at the ultramicroscopic level at postsynaptic sites of the rat brain. Brain Res. 2003;972:168–176. - PubMed
-
- Azzara AV, Sokolnicki JP, Schwartz GJ. Central melanocortin receptor agonist reduces spontaneous and scheduled meal size but does not augment duodenal preload-induced feeding inhibition. Physiol Behav. 2002;77:411–416. - PubMed
-
- Billington CJ, Briggs JE, Grace M, Levine AS. Effects of intracerebroventricular injection of neuropeptide Y on energy metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:R321–327. - PubMed
-
- Burlet A, Grouzmann E, Musse N, Fernette B, Nicolas JP, Burlet C. The immunological impairment of arcuate neuropeptide Y neurons by ricin A chain produces persistent decrease of food intake and body weight. Neuroscience. 1995;66:151–159. - PubMed
-
- Caspi L, Wang PY, Lam TK. A balance of lipid-sensing mechanisms in the brain and liver. Cell Metab. 2007;6:99–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

